

Strengthening Email Security Through Email Authentication
Jump back in time with me to 1971 when Ray Tomlinson sent the very first email. The need by Ray and the handful of people with whom he exchanged emails to prove they were the legitimate senders, likely never crossed their minds.
Email authentication has come a long way since then, starting with the introduction of SMTP in 1997 to counter rising spam, enabling mail servers to authenticate senders using usernames and passwords. Jumping ahead to 2003, SPF came on the scene to prevent email spoofing.
The Next Step in Protecting Email Integrity
This was followed soon by DKIM in 2004, allowing senders to sign emails using public key cryptography. Then a major milestone for email authentication in 2012, with DMARC proving to be a very effective tool leveraging DKIM and SPF to combat the relentless and exponential increase in phishing and spoofing cyber-threats.
Phishing and spoofing continue to remain a threat, have a look at these sobering statistics from Hornetsecurity’s recent Cyber Security Report:
- Phishing remains the top attack method, accounting for 33.3% of all email-based attacks
- Malicious URLs were used in 22.7% of email attacks
- Only 35.4% of email domains have implemented DMARC for email authentication
These numbers show that businesses must significantly improve efforts to protect their mail domains’ integrity. They must also configure, maintain, and monitor email authentication mechanisms properly.
What Is Email Authentication?
Let’s start by breaking down exactly what email authentication is, its purpose and why we should care. It’s essentially a process that uses various mechanisms and techniques to verify the origin of an email, and in doing so reduces email-based attacks such as spoofing and phishing.
At the start of this blog, we saw that email delivery lacked security in its architecture and design.
Its importance
As a critical tool for businesses, cyber-attacks via email pose a continued and significant threat, often used as a launching point for many other types of attacks. These attacks can have far-reaching consequences, may have legal implications, can lead to a loss of reputation, and have significant impact on a business’s brand.
How to Authenticate
Now, let’s dive deeper into the three key email authentication protocols I mentioned at the beginning of this blog:
- SPF
- DKIM
- DMARC
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC work together to prevent these threats by verifying the sender’s identity and ensuring the integrity of the message. All are configured as DNS records, each with a subtly different authentication mechanism, and used to protect against common BEC (Business Email Compromise) threats.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
SPF checks the sending server’s SPF record to verify if the email was sent from an authorized IP address. If the IP address is listed in the SPF record it passes the check, otherwise it fails.
It provides domain-sender authenticity by verifying that the source domain in the message matches the “Return-Path” field. Domain owners can then specify which mail servers are authorized to send email on behalf of their domain. This helps prevent domain spoofing, in other words attackers pretending to be sending emails from a trusted domain, when in fact they’re not.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
DKIM verifies whether the email is cryptographically signed with the sending domain’s private key. It then validates this against the corresponding public key. If the keys match, the check passes. If they do not match, the check fails. This process confirms that the domain owner sent the email without tampering during transit.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance)
DMARC performs a critical function of validating email authenticity using the checks in SPF and DKIM, providing a two-way assurance for both the sender and recipient. It uses a set of rules, referred to as “policies”, to instruct receiving mail servers on how to handle emails from that domain when they fail either SPF or DKIM checks (or both), effectively determining if an email is legitimate.
If an email does fail DMARC, one of these three options set in the DMARC policy instructs the action to take:
- Deliver the email
- Mark the email as spam
- Block delivery of the email
Below is a simplified representation showing how DMARC, SPF and DKIM work together in harmony:
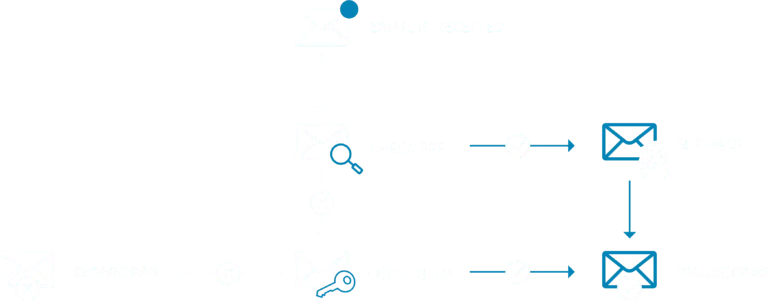
That last step, “DMARC Fail”, is when of those three actions I mentioned above come into play. Before I go any further through, now’s a good moment to talk about DMARC enforcement and its importance.
DMARC enforcement actively protects your domain and provides complete email security by choosing a protective action when an email fails DMARC. By contrast, setting the first action to deliver the email renders this policy ineffective and provides zero protection.
Setting the policy action however to mark the email as spam or reject is how we achieve DMARC Enforcement and really get the value from using DMARC for strong email authentication.
Have a read of this blog to do a deep dive into DMARC, and this one for more information and details of how SPF, DKIM and DMARC work together. If a video on this topic is what you’re after on the other hand, this podcast by Hornetsecurity on YouTube should answer all your questions and more!
Common Email Authentication Challenges
The assembly of a car is something that has always fascinated me, especially when cars were first produced.
The initial challenges of figuring out how to assemble all those moving parts must have been difficult. Similarly, implementing and ensuring effective email authentication presents its own set of challenges.
What kind of challenges do we face when configuring these and what could possibly go wrong? Well, quite a bit in fact.
Checking a successful implementation
To understand the complexities involved in an effective implementation, let’s flip around the equation by describing what a successful configuration of email authentication looks like. Put another way, how do we know it’s doing its job properly?
Here are a few methods or metrics we can use:
- The DNS records for SPF, DKIM and DMARC are configured with best-practice policies and are regularly reviewed and updated.
- Minimal disruption of email when transitioning to DMARC Enforcement
- Legitimate bulk emails are successfully delivered due to compliance with the authentication standards required by major email providers.
- Legitimate emails from a business’s domains reach the intended recipient inboxes instead of spam or junk folders.
- Visibility via a dashboard showing failure reports, alerts, insights, and analysis of email senders.
Phew, that’s quite a lot, isn’t it? The effort involved doesn’t really scale for a multinational with multiple domains and jurisdictions, and where successful email delivery is critical to the organization.
There are other consequences to consider besides just email delivery, one of them being an increase of phishing emails getting through. This article from Hornetsecurity goes into great (and sometimes scary) detail about the threat this poses. In fact, Hornetsecurity’s recent Cybersecurity Report found that out of the 45 billion emails we analyzed, phishing made up 43.3% of all malicious emails.
Brand protection
The ability of a DMARC Manager to reliably protect your brand and reputation cannot be understated. Significant and sometimes irrecoverable damage can occur if unauthorized emails, originating from your domain, contain offensive, misleading or fraudulent content.
Damage to an organization’s brand and reputation can be irreparable, not to mention the financial cost. IBM’s Cost of a data breach 2024 found that the average cost of a data breach globally is $4.88 million, with the USA sadly topping this list at $9.36 million, the healthcare industry bearing the most brunt.
How Hornetsecurity’s DMARC Manager Helps Businesses Implement Email Authentication
This all seems like a bit of a headache to manage and maintain effectively, which is where Hornetsecurity’s DMARC Manager can help.
It eliminates the pain of implementing and managing email authentication for organizations. It safeguards domains against email impersonation, phishing, and spoofing with intuitive DMARC, DKIM, and SPF management.
Here are some key features that make this comprehensive email protection solution from Hornetsecurity seem more like a way of life instead of an investment:
- Simplified implementation of DMARC – Guided setup of DMARC with step-by-step instructions, including integration with SPF and DKIM.
- Comprehensive reporting and analytics – Aggregated reports providing critical insights into email traffic and authentication results.
- Continuous monitoring and alerts – Real-time tracking of email authentication and alerting when critical issues occur.
- Protection from phishing and spoofing – Prevents malicious actors from impersonating your email domain and ensures only authorized senders can send from it.
- Compliance and best practices – Helps with meeting email security requirements across multiple regulatory environments, and actionable insights for optimizing email authentication and security.
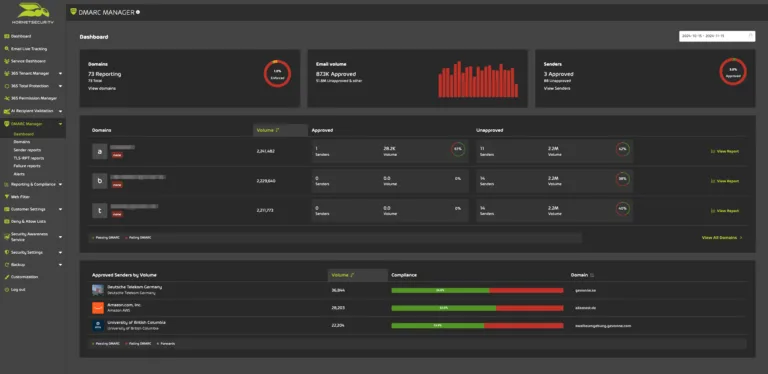
This screenshot showing off Hornetsecurity’s slick DMARC Manager gives you a sense of some of the possibilities when using this service.
Protect your organization from email spoofing and phishing attacks. With Hornetsecurity’s DMARC Manager, you can ensure email authenticity and strengthen your brand’s reputation.
Schedule a demo today to discover how Hornetsecurity can fortify your email security strategy.

Conclusion
Email spoofing and phishing attacks increasingly threaten us, and robust email authentication can stop many of these attacks. DMARC Manager from Hornetsecurity provides everything you need from a sophisticated solution such as this to enforce domain authentication and protect against email fraud, ensuring the integrity and trustworthiness of your communications.
Implementing and maintaining a strong security posture for robust and effective email authentication is a challenge. DMARC Manager makes it less so by empowering you to take control of your email security and maintain confidence in its communications.
Strengthen your email security today with Hornetsecurity’s DMARC Manager and experience the peace of mind that comes with knowing your email communication is secure and reliable.
Request a demo today and see how DMARC Manager safeguards your domains against email impersonation, phishing, and spoofing with intuitive management:
FAQ
Email authentication is a process that verifies the origin of an email using protocols such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, helping to reduce email-based attacks like spoofing and phishing.
DMARC enhances email security by validating emails against SPF and DKIM, allowing organizations to set policies on how to handle emails that fail authentication, effectively mitigating risks from phishing and spoofing.
Hornetsecurity’s DMARC Manager simplifies the setup and management of email authentication, provides real-time monitoring, comprehensive reporting, and protects against email spoofing, ensuring secure and reliable communications for organizations.

