Executive Summary
This month’s notable insights:
- Increase in malicious Excel attachments used in attacks due to Emotet.
- Reduction in industry threat index compared to last month but overall threat index still above last year’s average levels.
- Phishers attempt large-scale fraud through the impersonation of NGOs and Ukrainian refugees, asking for donations for Ukrainian refugees and war victims – mostly in Bitcoin. Similar and more targeted schemes have also been observed.
Summary
In this installment of our monthly email threat review, we present an overview of the email-based threats observed in March 2022 and compare them to previous ones.
The report provides insights into:
- Unwanted emails by category
- File types used in attacks
- Industry Email Threat Index
- Attack techniques
- Impersonated company brands and organizations
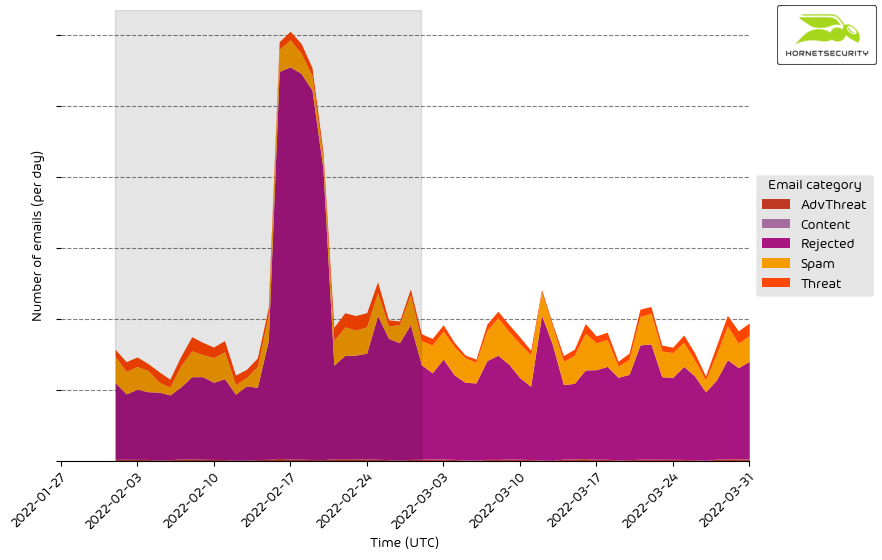
Unwanted emails by category
The following table shows the distribution of unwanted emails per category.
| Email category | % |
|---|---|
| Rejected | 72.98 |
| Spam | 20.55 |
| Threat | 5.27 |
| AdvThreat | 1.16 |
| Content | 0.04 |
The following histogram shows the email volume per category per day.
Methodology
The listed email categories correspond to the email categories listed in the Email Live Tracking of Hornetsecurity’s Control Panel. So our users are already familiar with them. For others, the categories are:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Spam | These emails are unwanted and are often promotional or fraudulent. The emails are sent simultaneously to a large number of recipients. |
| Content | These emails have an invalid attachment. The administrators define in the Content Control module which attachments are invalid. |
| Threat | These emails contain harmful content, such as malicious attachments or links, or they are sent to commit crimes, such as phishing. |
| AdvThreat | Advanced Threat Protection has detected a threat in these emails. The emails are used for criminal purposes and involve sophisticated technical means that can only be fended off using advanced dynamic procedures. |
| Rejected | Our email server rejects these emails directly during the SMTP dialog because of external characteristics, such as the sender’s identity, and the emails are not analyzed further. |
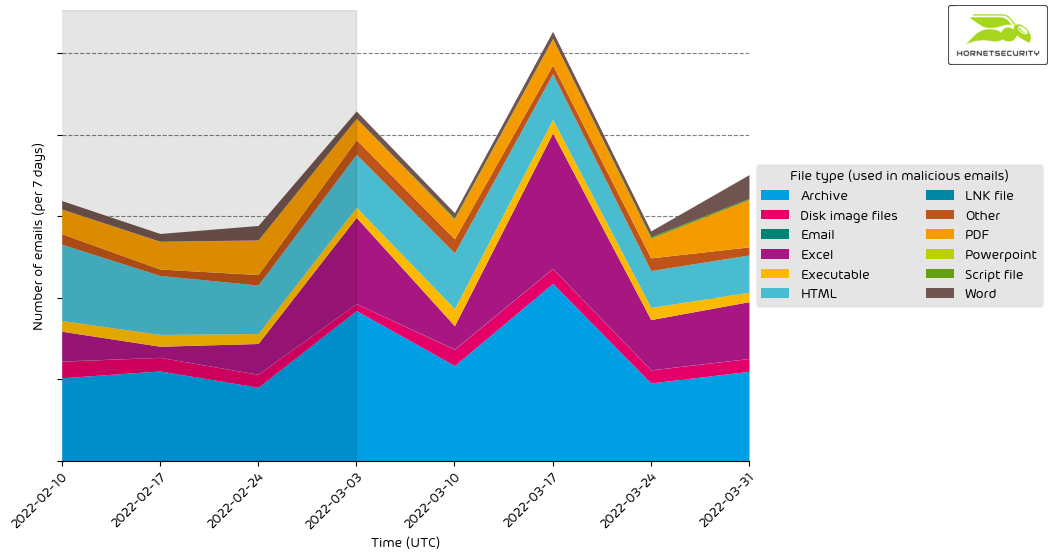
File types used in attacks
The following table shows the distribution of file types used in attacks.
| File type (used in malicious emails) | % |
|---|---|
| Archive | 36.9 |
| Excel | 22.3 |
| HTML | 14.7 |
| 9.4 | |
| Disk image files | 4.8 |
| Executable | 4.4 |
| Other | 3.7 |
| Word | 3.5 |
| Script file | 0.4 |
| 0.1 | |
| LNK file | 0.0 |
| Powerpoint | 0.0 |
The following histogram shows the email volume per file type used in attacks per seven days.
Attacks using HTML attachments continued to decline from 33.6 % to 14.7 %. The continued increase in malicious Excel attachments from 12.4 % to 22.3 % can still be attributed to Emotet currently spreading with malicious Excel documents.
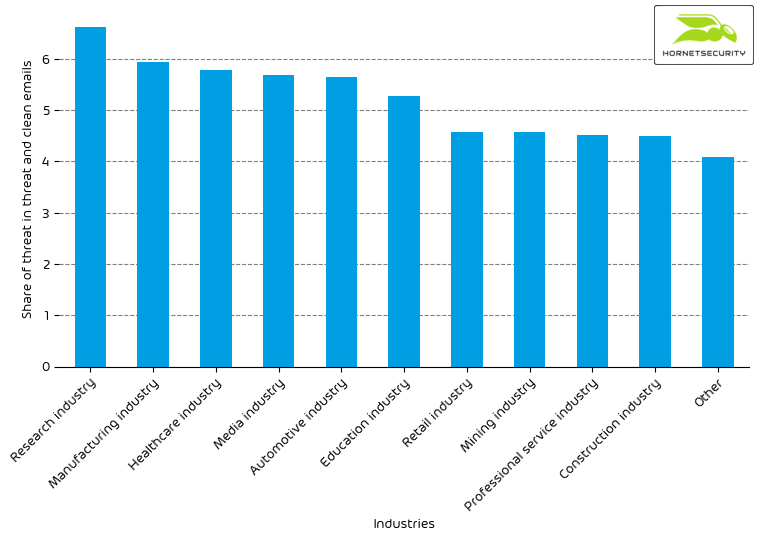
Industry Email Threat Index
The following table shows our Industry Email Threat Index calculated based on the number of threat emails compared to each industry’s clean emails (in median).
| Industries | Share of threat in threat and clean emails |
|---|---|
| Research industry | 6.6 |
| Manufacturing industry | 5.9 |
| Healthcare industry | 5.8 |
| Media industry | 5.7 |
| Automotive industry | 5.6 |
| Education industry | 5.3 |
| Retail industry | 4.6 |
| Mining industry | 4.6 |
| Professional service industry | 4.5 |
| Construction industry | 4.5 |
The following bar chart visualizes the email-based threat posed to each industry.
Even though its threat index dropped from 10.5 % to 6.6 %, the research industry remains the most threatened industry. The median threat index of all industries declined slightly from 4.9 % to 4.2 %. For comparison, the overall median threat index of all industries for the year 2021 was 4.0 %. This means even though we see a drop from last month’s elevated values, the values are still above last year’s average.
Methodology
Different (sized) organizations receive a different absolute number of emails. Thus, we calculate the percent share of threat emails from each organization’s threat and clean emails to compare organizations. We then calculate the median of these percent values for all organizations within the same industry to form the industry’s final threat score.
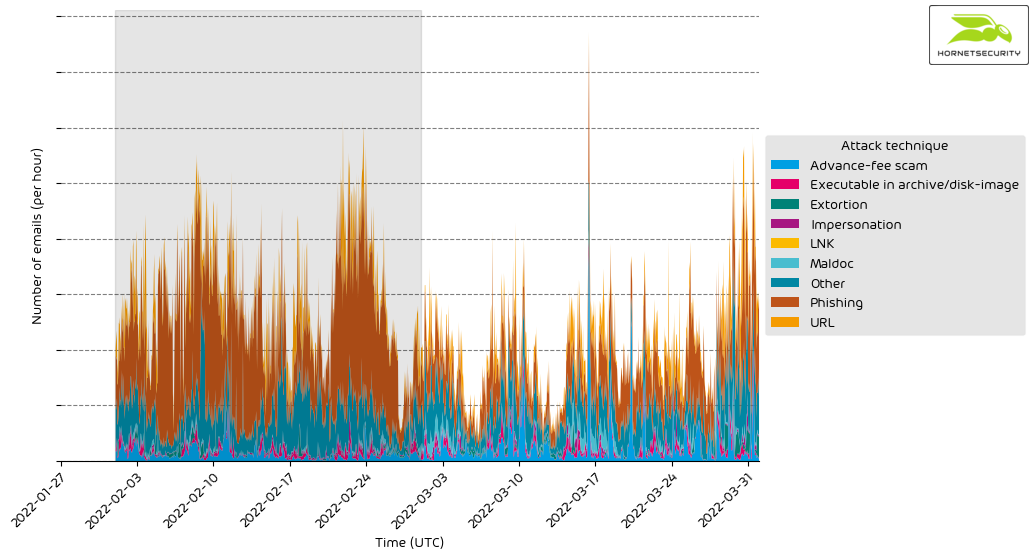
Attack techniques
The following table shows the attack techniques used in attacks.
| Attack technique | % |
|---|---|
| Phishing | 36.1 |
| Other | 28.5 |
| URL | 12.1 |
| Advance-fee scam | 11.8 |
| Executable in archive/disk-image | 3.4 |
| Maldoc | 3.3 |
| Extortion | 2.7 |
| Impersonation | 2.1 |
The following histogram shows the email volume per attack technique used per hour.
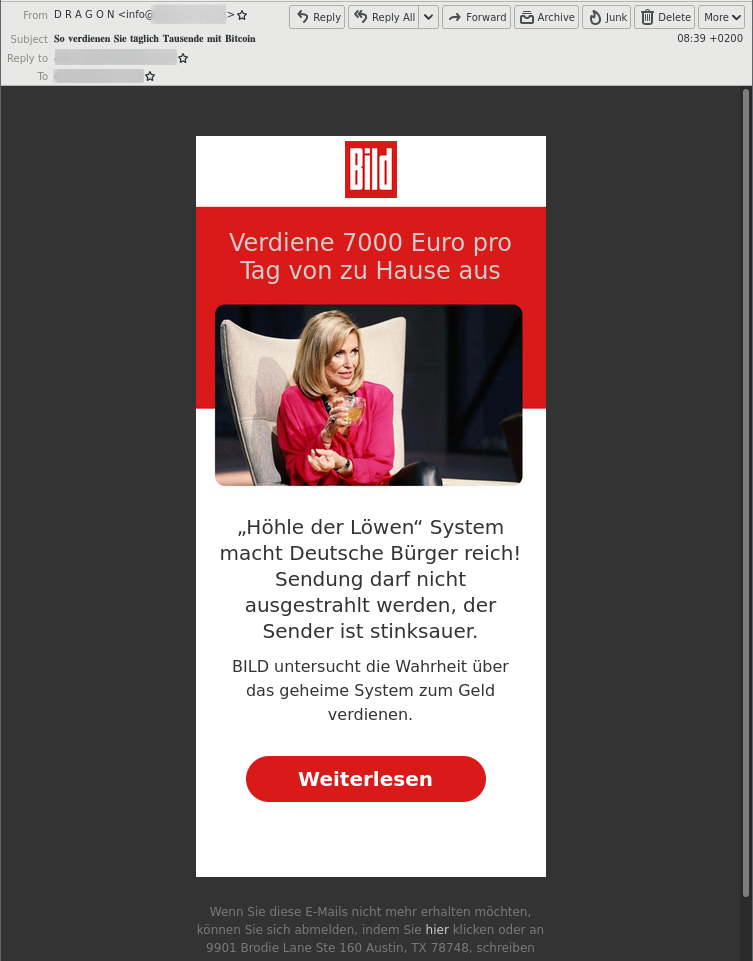
The spike on 2022-03-16 in advance-fee scams is caused by emails referencing the German investment TV show “Höhle der Löwen” (German’s version of the British Dragon’s Den or the US Shark Tank TV show). The emails claim an investment opportunity that was too good and therefore banned from airing on the TV show.
The attackers try to lure the victims into “investing” in a Bitcoin trading bot or, in some other way, transfer money to the attackers in exchange for significant monetary returns. The financial returns are not true, and the offer is a scam.
The emails were sent in a concise time span, causing this sharp spike in the data. This advance-fee scam campaign’s other less pronounced activity spikes were on 2022-03-03, 2022-03-10, 2022-03-20, 2022-03-26, and 2022-03-31. However, the email volume per hour was smaller than for the campaign on 2022-03-16.
Impersonated company brands and organizations
The following table shows which company brands and organizations our systems detected most in impersonation attacks.
| Impersonated brand or organization | % |
|---|---|
| Sparkasse | 66.7 |
| Other | 11.7 |
| Amazon | 7.6 |
| Deutsche Post / DHL | 3.1 |
| Volks- und Raiffeisenbank | 3.1 |
| Postbank | 2.4 |
| Fedex | 1.6 |
| 1.4 | |
| Dropbox | 1.0 |
| Microsoft | 0.9 |
| Strato | 0.5 |
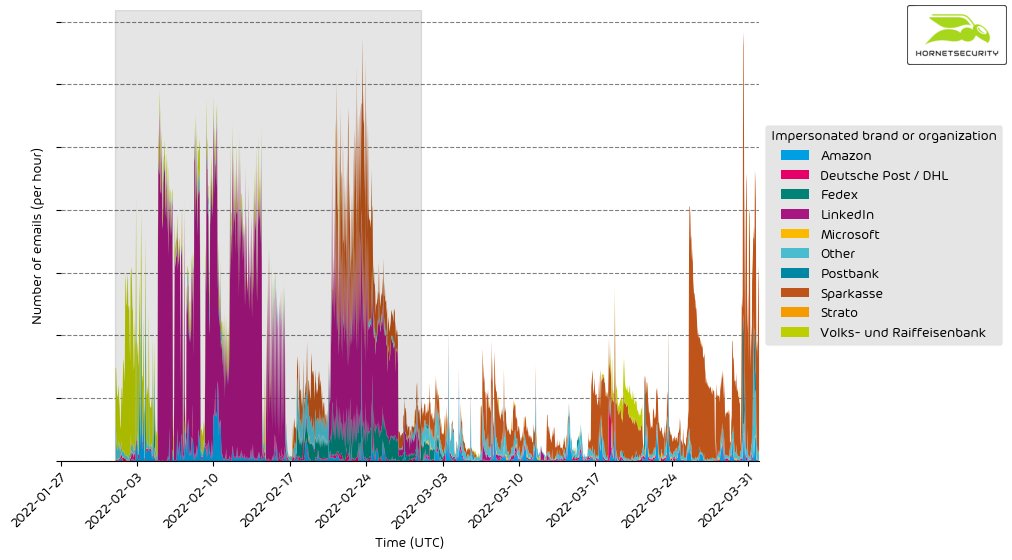
Hornetsecrurity observed a new peak of NGO (e.g., ‘Other’ as seen above) scams this month. The ongoing war in Ukraine lures fraudsters into the mix. Fraudsters impersonate NGOs and Ukrainian refugees to gather US Dollars or Bitcoin donations. In general, in times of crisis, fundraising scams are imminent.
The following histogram shows the email volume for company brands and organizations detected in impersonation attacks per hour.
After last month’s large-scale LinkedIn phishing campaign, the German Sparkasse bank again takes first place for most impersonated brand in attacks.