

How Artificial Intelligence (AI) is Changing Cybersecurity
Traditional security systems can’t keep pace with the increased number of cyber threat activities.
The amount of data that is being generated is large and complex. According to the Data Never Sleeps 4.0 report 2016, over 18 TB of data is generated every minute. Today, that number is even higher.
We can’t analyze this amount of data by ourselves. We need help. We need Artificial Intelligence (AI).
This article is about Artificial Intelligence (AI) for cybersecurity, understanding the basics, advantages and disadvantages, use cases and real-world scenarios, and some predictions of how the future of cybersecurity with AI will look.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence is a set of technologies that can learn from provided data and draw conclusions or decisions. AI can’t work alone, it requires data. Depending on the data that is being used, AI can make right or wrong decisions.
It is used in different industries, from the auto industry, and medicine, to technology. AI works in three ways:
- Assisted intelligence
- Augmented intelligence
- Autonomous intelligence
It consists of four subsets including:
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- Neural Networks
- Expert Systems
i.e., it encompasses a range of techniques and approaches, each with its own variations.

Machine Learning (ML) uses statistical techniques to learn from the data. It works better with single tasks than comprehensive missions. Some of the use cases of machine learning are product recommendations in e-commerce shops, image recognition, virtual personal assistants, and others.
Deep Learning (DL) is a subset of machine learning that helps analyze complex data and draw conclusions based on them. For example, Alexa or Siri uses deep learning to understand your speech and language when you speak to them.
Neural Networks teach computers to process data in a way similar to how our brains do. They consist of large amounts of connected nodes that are trained to recognize patterns in input data. Neural networks are used in combination with deep learning in voice and image recognition, language translation, and others.
An Expert System is a computer system that mimics specific human behavior in a particular field. Some examples of expert systems are the Intelligent Tutoring System (ITS), Cancer Decision Support Tool (CaDet), Knowledge-Based Expert System, and others.
Applying AI to cybersecurity means analyzing data from security incidents, learning from it, and then applying the solution to a new attack to prevent it.
Artificial Intelligence vs. Data Analytics
Even though they are related, artificial intelligence (AI) for cybersecurity and data analytics (DA) are two distinct fields. They differentiate in the way they work with the data.
Artificial intelligence’s (AI) primary role is to replicate human-like cognitive behavior. AI uses machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, robotics, and data analysis to improve itself. It continuously analyses data and learns from it. It is dynamic and iterative.
On the other hand, Data analytics (DA) is static, it uses statistical techniques to identify trends, collaboration, and patterns in data. Data analytics predicts patterns based on historical data to foresee future events. Data analytics is not iterative or self-learning like AI.
Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics do not complete with each other, they complement each other.
Advantages & Downsides of AI in Cybersecurity
Everything has pros and cons, including AI. AI is already used in cybersecurity and here are some things we have learnt.
Some of the benefits of using AI-powered security systems are real-time threat detection and predictive analysis, anomaly detection, automation and orchestration of repetitive tasks, better end-point protection, AI-enabled authentication, and improved and enhanced threat detection and response.
All of these enhancements work based on the established baseline through repeated training processes. AI assists us in becoming more proactive and staying safer than we were previously.
Everything sounds perfect; is there any downside to using AI in cybersecurity? Well, yes, there is.
Malicious cybersecurity professionals can misuse AI and teach it how to take actions that are in their favor. This is called Adversarial AI attacks. That is a type of attack where the attacker manipulates a machine-learning model by making minor changes to the input data.
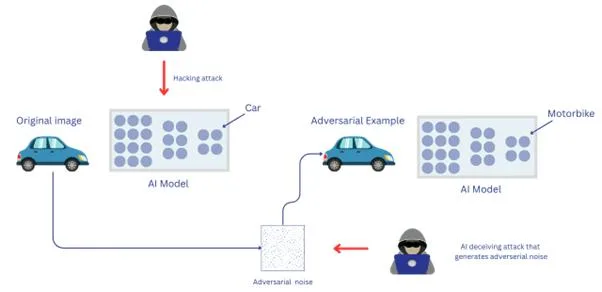
An attacker can manipulate the system using image and text classification and malware evasion. This hurts autonomous vehicles, medical imaging, and security systems. Google, Amazon, Microsoft, and Tesla have faced adversarial attacks in the past.
Did you hear about AI-enabled botnets? AI can be used to create botnets that can coordinate attacks, execute DDoS attacks, and credential stuffing. They are intelligent and can adapt their behavior based on changes in the environment and avoid detection.
AI learns from human behavior and mimics or replicates it. What if the actions are based on biased and flawed data? This can lead to wrong actions. One way to handle this properly is by having experienced cybersecurity professionals on our teams.
AI works with a large amount of data, and very often involves personal and sensitive data. This raises privacy concerns and breaches. We need to ensure that our data is fully secured against any breaches. We don’t want malicious people to get our AI model in their hands.
Best Practices for Implementing AI in Security
AI is a powerful tool in our hands, and to achieve its purpose, it should follow the best practices.
Firstly, you should choose the right machine learning or deep learning models that meet your security objective.
Secondly, it is about data quality. AI draws conclusions and actions based on the provided data through the repetitive training process. If data are flawed, it means AI actions will make flawed decisions. That can cause more trouble than benefits. Data should be high-quality reflecting real-world conditions.
Implement a mechanism that minimizes or avoids false positive conclusions and alarms. The primary purpose of AI in security is to predict real threats.
Since representative data is sensitive, you should ensure data is stored in a secured location and encryption and access control are in place.
Additionally, your data collection and storage need to comply with policy regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and others.
Even if the AI model complies with policy regulations, you should ensure you regularly perform auditing.
Furthermore, even if high-quality data are used to train AI models, AI models should be regularly tested and updated to meet the latest trends. This is a crucial step since cybersecurity threats are evolving while you are reading this blog article.
There are more practices such as integration of AI model with threat intelligence, explainability and transparency of AI decisions, scalability, redundancy and resilience, collaboration with security professionals, and others.
Use Cases of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
There are numerous use cases where we can take leverage of AI in cybersecurity. We will name a few and share with you some real-world examples.
In general, AI helps to detect unusual patterns and behavior that may indicate security threats. It does it through anomaly detection, behavior, and predictive analysis.
Furthermore, based on the established baseline and repetitive training process, it can detect unknown malware and malicious user actions (e.g. QA code scams) based on their behavior.
It does detect phishing emails and fraud detection in real-time by preventing them immediately and learning from their behavior.
Today, we can see AI implemented in IDS (Intrusion Detection System) and IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), network and endpoint security, SIEM (Security Information and Event Management), security automation and orchestration, vulnerability and patch management, DLP (Data Loss Prevention) and more.
AI is used by vendors who offer security protection such as Microsoft, Google, AWS, Fortigate, Palo Alto, Hornetsecurity, and others.
In March 2023, Microsoft introduced Microsoft Security Copilot powered by AI. It uses AI to detect threats, manage incidents, and improve security. Microsoft also integrated AI with other security products such as Microsoft Defender for Endpoints. It uses AI-adaptive protection which identifies devices at risk and blocks them accordingly.
IBM uses an AI model in their IBM Security QRadar SIEM solution. IBM Security QRadar SIEM in combination with AI helps you to analyze, detect, and prevent cybersecurity threats faster and automate tasks.
Fortinet provides AI-driven SOC. Their portfolio provides advanced threat detection and response, centralized monitoring, and automation through Fortinet devices. It reduces endpoint security risks through early detection and prevention.
Hornetsecurity uses AI to validate email recipients. Here is what it says in the document: “AI Recipient Validation is an AI-based, self-learning service that continuously analyzes a user’s email communication patterns in the background. It automatically detects potentially unintended recipients, warns about emails containing sensitive data like Personal Identifiable Information or inappropriate wording, and factors in user behavior and responses to automatically adjust warnings and suggestions issued in upcoming communications.”

While we are discussing IT Security, I would like to take this opportunity to share in-depth insights about different cybersecurity threats in our Cyber Security Report and Ransomware attacks survey.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
In the future, AI will be adopted as a standard in the cybersecurity industry, just like in many other areas. With just traditional security tools and humans, we can’t and won’t be able to follow evolving cybersecurity threats.
It is promising, but also challenging what AI will bring to the table. It will be smarter based on the huge amount of data that will be generated until then. Based on some cybersecurity vendors, AI might be able to respond to its action by shutting down the affected machine, isolation the affected machine from the network, and apply countermeasure response to the source of the attack.
We see more and more IoT, IIoT, and OT integrated into traditional infrastructure. This will have security implications and AI will be needed to make the right cognitive decision and prevent attacks.
Everything we named as a use case in the previous section will be enhanced and better.
AI has the potential to improve cybersecurity and make our data safer.
What the future brings with more AI we don’t know, but it might have an impact on the job market. It also brings ethical and data privacy concerns and more adversarial attacks.
o properly protect your cyber environment, use Hornetsecurity Security Awareness Service to train your employees to become aware of AI threats and assist in securing your critical data.
To keep up to date with the latest articles and practices, pay a visit to our Hornetsecurity blog now.
Conclusion
AI is already used in many cybersecurity tools and services and will have an even larger role to play in the future. Adversaries are also adopting AI to automate and improve their attacks.
In this article you learnt about the different ways AI can be used, both for attack and defense, and it’ll be an important evolution to keep an eye on for the cybersecurity field.
FAQ
Artificial intelligence’s (AI) primary role is to replicate human-like cognitive behavior. Ai is used in cybersecurity for real-time threat detection, behavior and prediction analysis, anomaly detection based on the established baseline, automation and orchestration of repetitive tasks, better end-point protection automation and more.
Yes, we can. AI is already used in cybersecurity to enhance threat detection and predictive analysis. It analyses data and makes decisions based on it.
AI uses machine learning, deep learning, neural networks and expert systems. They work together to learn from data, make better decisions and protect our digital assets.

