

Remote Management Survey
1 in 5 I.T. pros say remote workers are not secure, survey finds
Key takeaways from the 2022 Remote Management Survey by Hornetsecurity
- 18% of I.T. professionals believe that remote employees are not working securely and that company data is at risk
- 8 out of 10 I.T. professionals believe that remote working conclusively introduces cybersecurity risks that are otherwise not present.
- According to 3 out of 4 I.T. professionals, employees are using personal devices to access sensitive company data
- 1 in 3 organizations does not provide cybersecurity awareness training to remote employees
- 1 in 6 organizations has suffered a cybersecurity incident directly related to remote working
About the 2022 Remote Management survey
As part of our effort to remain in touch with the current state of the IT industry and to keep our finger on the pulse of the frequent and drastic shifts that come with it, our team at Hornetsecurity conducts a survey every few months. Each survey concerns a specific topic that we think is essential to the industry, and to business entities of all kinds and in all parts of the world.
No shift has impacted the way many organizations operate than remote work and the subsequent need for remote management. While the concept of remote work is not new to the industry, the 2020 pandemic has supercharged its adoption around the world and across industries. This has led to organizations changing, seemingly overnight, to remote working setups which have introduced a host of cybersecurity concerns that were not viable threats until now.
Our 900+ survey respondents come from a multitude of industries, regions, differing years of experience, and from companies of varying sizes.
Remote Working in 2022
Initially brought to the mainstream workplace as a pandemic measure, remote working has become a staple of the modern working environment, in addition to remote monitoring and remote team management. With more companies opting for either a fully remote or hybrid approach to work, the shift towards remote work over the last few years is extremely well-documented, and all the evidence points to it being a permanent employment fixture for the foreseeable future.
Remote work has therefore become one of the most fundamental aspects for the workplace, both from the perspective of employers and employees. While a recent survey by Buffer shows that 97% of remote workers would like to continue doing so for the rest of their career, employer opinion on remote work tends to vary, with 72% of employers in the United States preferring that their employees work within an office environment, and only 12% of leaders considering employees as productive working remotely as they are in the office, despite evidence to the contrary.
Other employers cite security concerns as their primary motivation for bringing office workers back to the office, with a 37% increase in data breaches in the third quarter of 2022. That said, this is a significant decrease from the 125 million data breaches that occurred shortly after the beginning of widespread remote working, proving that companies that invested in good cybersecurity practices and remote team management tools had an immediate effect on risk within their organizations.
Regardless of employer opinion, the overwhelming response to remote work from an employee perspective has been positive. Over 57% of employees cite that they would leave their job if remote work or hybrid working was not an option for them; 84% state that they would take a pay cut in order to retain their work from home privileges or to work for a company that allowed them to work remotely. The biggest benefit to working from home for employees is the flexibility that it allows them, with 67% claiming that the flexibility in their lives had led to a better work-life balance.
While remote work does come with its own set of challenges for employees, such as struggling to create and then maintain that balance, it is overwhelmingly clear that remote and hybrid working is here to stay, and therefore organizations need to be prepared to face the challenges that remote management brings from a security perspective.
The immediate increase in cybersecurity breaches at the onset of remote working, and its subsequent decrease as companies shifted their investments into better security training and cybersecurity measures, proves that remote working can be as safe as working from the office, provided the employees and employers both have the training to adhere to stricter measures. In 2021, this was primarily implemented with multiple authentication measures for endpoints and servers, as well as a boost in security training. These are measures that need to be built on, and improved upon, for a better secure workplace in general, but companies with remote or hybrid work policies need to give better cybersecurity measures a stricter priority for 2023.
Close to 1 in 5 I.T. professionals (17.9%) say workers are not secure when working remotely

According to our remote management survey, a significant number of I.T. professionals are aware of their remote security shortcomings and have a decent understanding of both security issues that have been introduced alongside the rise in remote work and that the solutions to these threats have not been fully implemented within their organization, despite the significant increase in remote working worldwide.
This is likely due to a combination of the rapid and sudden expansion of remote work over the past few years, and businesses struggling to keep up with all the infrastructural and operational changes that this has brought with it. Unfortunately, I.T. security tends to be of a lower priority in comparison to essential tasks that must be upgraded and adjusted in order to ensure business continuity – at least, until they suffer a cybersecurity breach.
3 in 4 IT professionals (73.8%) say that employees can access sensitive work-related data through their personal devices

One of the most surprising insights collected from this survey is the extremely high use of personal devices among employees to access sensitive data. The vast majority of these cases are likely to be users accessing emails and documents on their personal mobile phones while using systems such as Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, or other cloud-based office applications – a situation that makes remote management a significantly more thorny issue.
While not necessarily associated with the rise in remote work, this identifies that there is a significant amount of sensitive data that is at risk of being compromised through a variety of techniques targeting end-user personal devices. Endpoint configuration / management is fairly uncommon when it comes to worker’s personal devices due to the legal and ethical issues that come along with providing those services on non-company owned devices. It also highlights the importance of cloud-based security features rather than the use of on-device features.
14% of respondents said their organization suffered a cybersecurity incident related to remote working

As we discovered in previous surveys over the past few years, it’s clear that cybersecurity incidents are on the rise. While the situation is slightly less dire than it was in the immediate wake of the pandemic, the incidence rate is still high. Therefore this finding, while still relatively alarming, should come as no surprise. It means that 1 in every 6 companies has suffered a cybersecurity incident specifically related to remote working.
While the exact cost of each of these incidents is unknown, industry data from IBM indicates that major data breaches in 2022 cost their victims an average of $4.35 million, a 2.6% rise from the 2021 average of $4.24 million. This takes into account the potential ransoms paid through ransomware, the cost of the significant down-time that a data breach can cause, and industry fines that can be levied against companies that fail to protect sensitive data.
What are the main sources of remote work related cybersecurity incidents?

28.1% of our remote management survey respondents reported that ‘compromised endpoints’ and ‘compromised credentials’ were the main reason for security incidents.
When it comes to compromised endpoints, the explanation is fairly obvious – as users travel and work in different locations, there is a higher possibility of losing devices that contain sensitive data. The risk of this is intensified when one considers the relatively high amount of personal devices that have access to sensitive data that do not have any endpoint configuration to help protect against unauthorized access.
Credentials becoming compromised through the threats of social engineering and email phishing attacks are also equally common. Remote working exacerbates this risk as users are more isolated and less likely to be able to identify threats alone. In comparison, those in the office may have more instant access to other colleagues who can help verify communication before communicating sensitive information. The solution to this particular issue is two-pronged. Firstly, a robust email security suite can eliminate a significant portion of inbound threats before they even reach end-users. For the threats that do reach their intended target, cybersecurity awareness training such as the programs offered by Hornetsecurity can hugely impact the potential of a data breach.
15.7% of respondents also cited uncontrolled file sharing as a source of cybersecurity incidents. Cloud storage platforms have become essential for remote work operation, but sharing access to files on these platforms with third parties introduces significant risks. User error that results in access being provided to sensitive company data to unauthorized individuals is a serious risk, and is relatively common. Stringent access and authorization processes need to be put in place in order to avoid such occurrences.
Just over 1 in 10 (11.6%) of respondents that reported a remote-work related cybersecurity incident said that unsecured or public networks were the root cause. While endpoint security might be in the control of most I.T. departments, the networks that users connect to add another layer of risk that is not always accounted for. While relatively uncommon, users could be victim to attacks such as Wi-Fi spoofing in public areas. For example, a cybercriminal may name a remote Wi-Fi hotspot the same name as a local coffee shop, tricking users into joining said network and compromising their endpoints.
The least common source of cybersecurity incidents per this survey was lack of physical security or privacy in public places. While this is an extremely low-tech form of cyber attack, it was still reported by nearly 1 in 10 of incident victims. This serves as a reminder that there are some security considerations that cannot be handled through any digital remote management tool, and rely solely on users’ awareness of their surroundings.
Which companies are most at risk of remote work cybersecurity incidents?
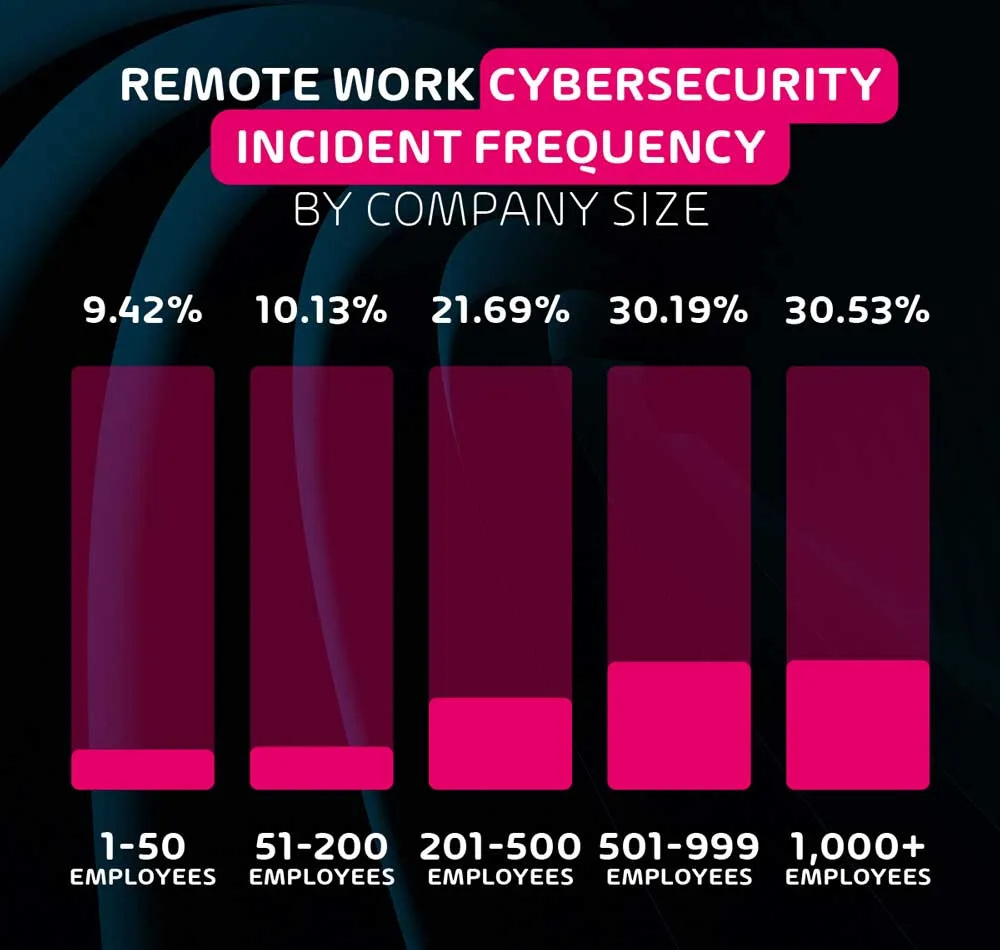
The data gathered through this survey very clearly indicates that the larger the organization, the more likely it is to have suffered a remote cybersecurity incident. In fact, organizations with 500+ employees are 3 times as likely to have an incident than SMEs with less than 50 employees.
This goes to show that while cybersecurity is practically infinitely scalable, size always increases risk. It also indicates that black hat hackers are significantly more interested in attacking large organizations – likely due to a higher potential return for their effort, and the thrill of successfully attacking a known organization.
Almost half (47.6%) of employees in the respondents’ organizations work remotely

When asked what percentage of their organization’s workforce operates remotely in some capacity, the average of our respondents’ answers worked out to nearly half – 47.6%. While not entirely surprising, this is a very high percentage, especially when one considers this percentage is set to increase over the next few years.
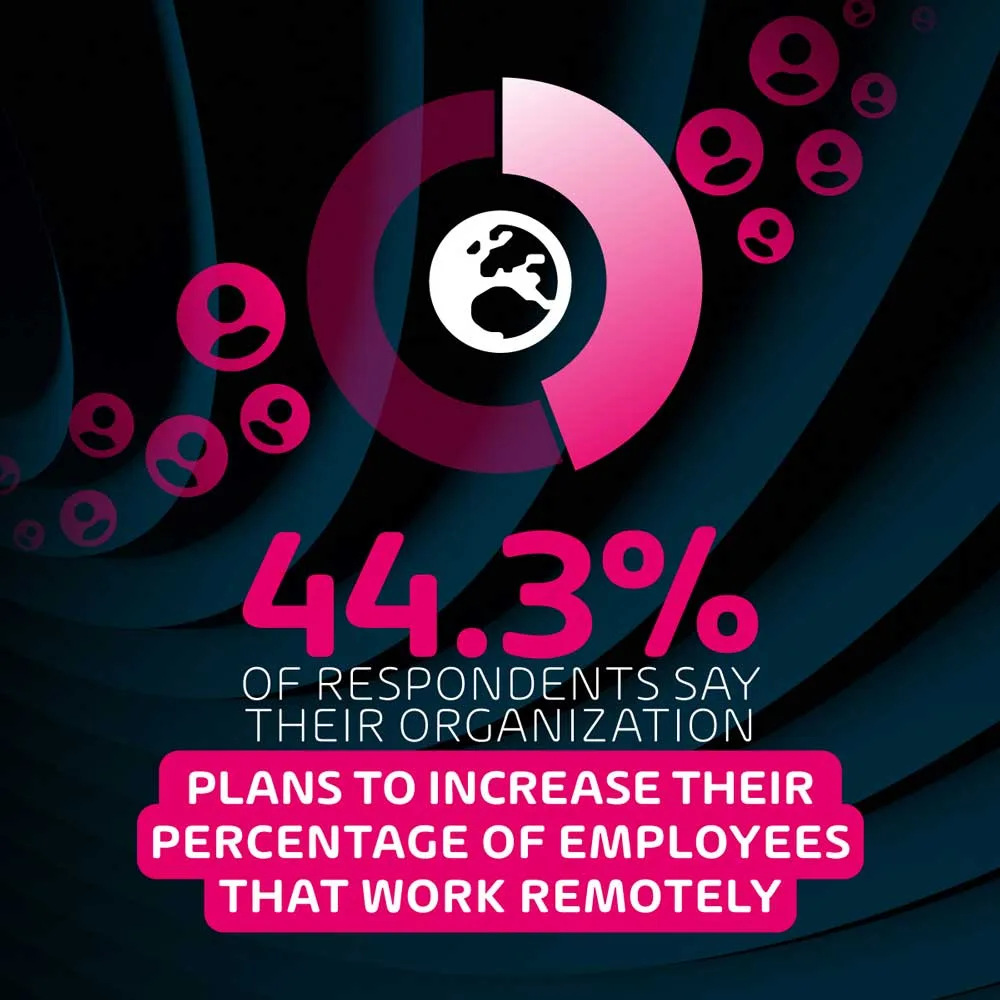
This further indicates the necessity for large organizations to take a slightly different approach to cybersecurity in order to cater for the nuances of remote work, and invest further in making sure remote employees are aware of the increase in risks. Cybersecurity has always required users to play their role in preventing incidents – the increase in remote work and remote team management has expanded this role, as security administrators now have slightly less overall control over the environment in which users are working.
4 in 5 IT professionals (79.5%) think that remote work introduces cybersecurity risks that are not present when working on-premise

Our cybersecurity experts at Hornetsecurity are adamant that remote cybersecurity introduces additional risks in comparison to on-premise security. While nearly 80% of our respondents agree with this, this survey reveals a cohort of 12% of I.T. professionals that don’t agree, and another cohort of 8.5% that are unsure.
This is relatively surprising considering that some of the sources of cybersecurity incidents found in this survey are practically unique to remote workers. This may indicate a lack of awareness or understanding of these potential risks among I.T. professionals. That being said, the vast majority of respondents are aware of the risks.
1 in 3 organizations do not provide any cybersecurity awareness training to users who work remotely

While I.T. professionals are mostly aware of the additional risks associated with remote work, this survey reveals that organizations aren’t yet investing enough in user awareness. 1 in 3 organizations do not provide cybersecurity training to remote employees, and considering that the main sources of cybersecurity incidents reporting within this survey are user-dependent, this may be a significant oversight.
Data from many of our previous surveys, especially ones surrounding cybersecurity incidents such as ransomware, consistently indicates that while the security tools and remote management services used by an organization are essential, the most vulnerable link in the security chain is consistently the users.
Our latest ransomware survey showed that 1 in 4 organizations had been the subject of a ransomware attack, and 3 in 4 of these attacks were caused by user error (either through phishing/email attacks or compromised endpoints). The importance of user training cannot be overstated.
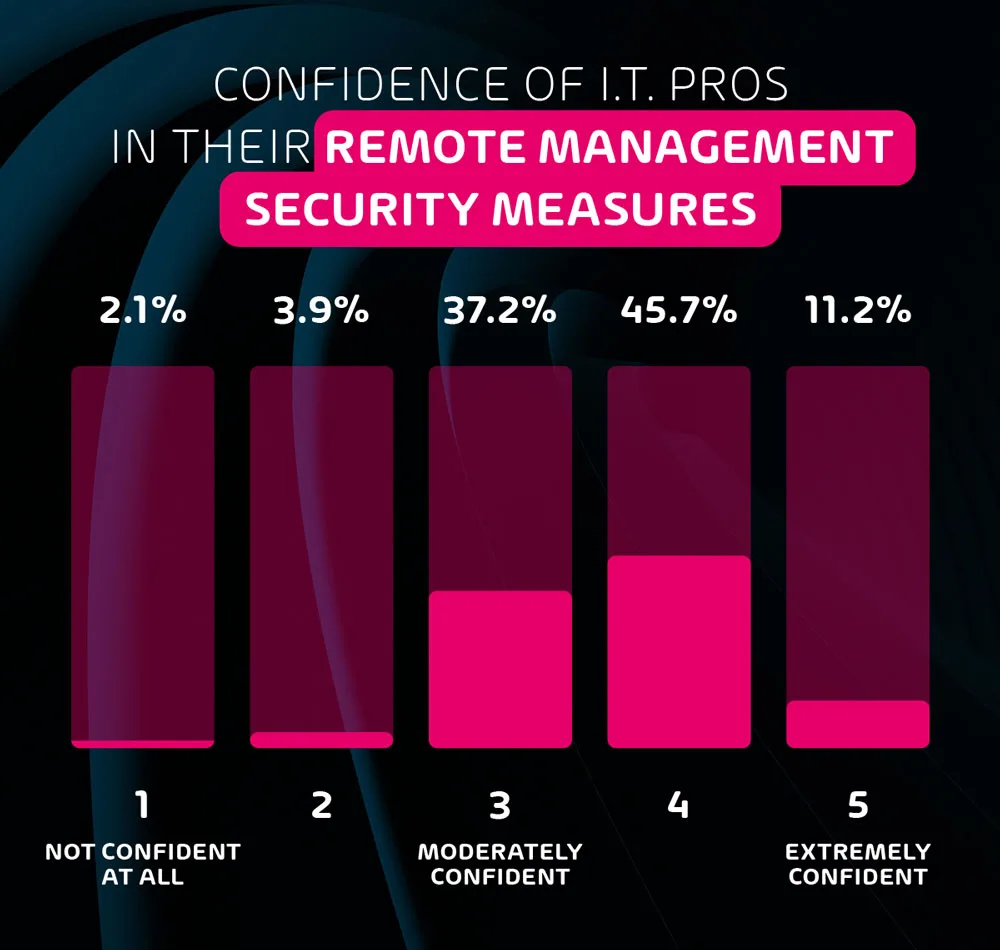
How confident are IT professionals in their remote security measures?

Despite the very clear risks associated with remote working and remote team management, I.T. professionals reported a high overall confidence level when it comes to the security of their remote employees. On a scale from 1-5, the average confidence level among respondents ranked at 3.6. Considering the lack of cybersecurity awareness training offered to employees, and the fact that 20% of respondents don’t think that remote work poses additional security risks, this confidence is likely misplaced.
What are the most commonly used security features for remote management?
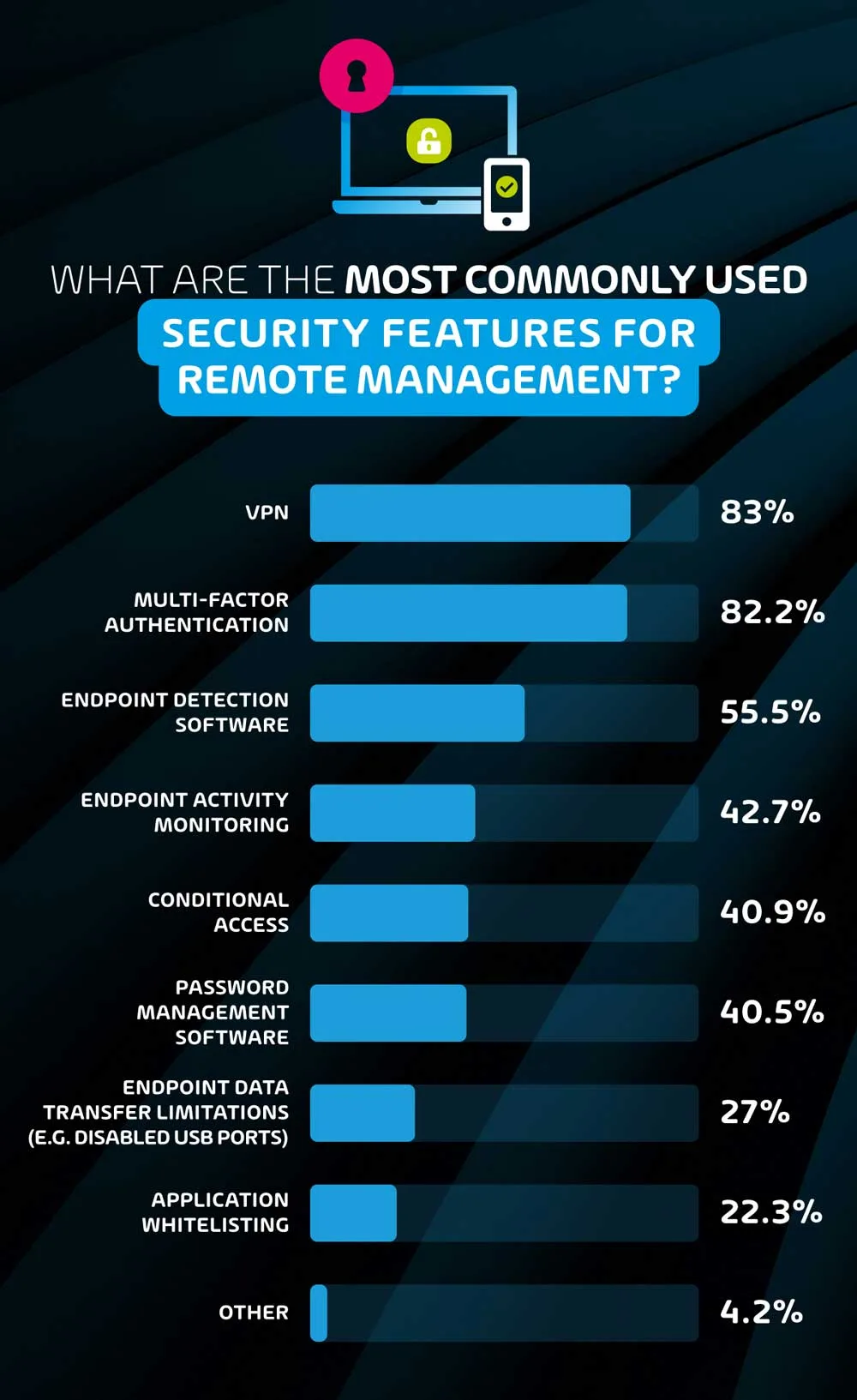
When asked for the most common security features used, VPN came out on top. However, one should keep in mind that while VPN does indeed provide further security, its function is often essential for employees to access systems and storage that are only available through on-premise networks, and this would explain the very high usage rate.
The most common security-specific feature was Multi-Factor Authentication – this comes as no surprise, seeing that platforms such as Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace provide this feature natively. While just over 4 in 5 respondents reported using this feature, it’s worth noting that a motivated black hat hacker can find a way around this relatively easily – in fact the top two sources of cybersecurity incidents reported in this survey – compromised endpoints and compromised passwords – should theoretically be halted by MFA, but clearly are not. That being said, not having MFA would be extremely unwise, as it protects from low-level attacks.
Endpoint detection software was the third most popular security feature, with 55.5% of respondents reporting its use. This software is practically essential for users with direct access to network systems or storage, and is an indispensable tool for large organizations that must monitor a nearly endless number of devices.
Endpoint activity monitors are a slightly thornier issue. While activity monitors provide useful data for I.T. security teams, they can also be seen as unnecessarily intrusive for remote workers. Employers often use security as an excuse to be able to monitor employee activity to ensure that they’re working. Based on the results of this survey, this is most prevalent in North America where nearly half (47%) of organizations use remote monitoring and remote team management in comparison to 39.7% of European companies. This data point corroborates the existing sentiment of the stricter corporate culture and employee inflexibility in the US as opposed to their EU counterparts.
41% of respondents indicated that their I.T. team uses conditional access and password management software to mitigate risks for remote workers. The former blocks users from accessing certain systems or data based on whether their device/identity state fulfills specific criteria. This system is particularly for I.T. teams that are looking to more directly reduce the risk of users accessing data from unusual locations or un-approved devices that could lead to a potential compromise of data.
That being said, more complex conditional access configurations often increase frustration among less tech-savvy employees that may not understand why they cannot access their data under certain conditions, increasing the time I.T. teams must spend configuring devices and tending to users. Password management software is another human-focused solution, and considering that this survey found that compromised passwords was a top source of cybersecurity incidents, it should likely be used more often.
The least reported cybersecurity measures were endpoint data transfer limitations and application whitelisting with 27% and 22.3% of respondents reporting their use respectively. Both measures impose further restrictions on endpoints and therefore users in the name of security, and while they may be worth the inconvenience to users, there are many organizations (especially smaller ones) that require their users to be more flexible, and these features may not be practical. For larger organizations with more defined user roles and responsibilities however, these should be used more frequently.
How do organizations handle device management for their remote employees?

For practically all of the cybersecurity and remote management features mentioned in the previous section, endpoints must be configured by the I.T. department before being deployed to users. This survey, however, indicates that nearly 1 in 4 organizations do not handle endpoint configuration from start to finish before providing said device to their employee.
15.3% of all respondents said that their employees use their own devices with ‘some’ endpoint configuration for remote work. 6.4% of respondents said employees used their own devices with no configuration at all. While not procuring and configuring endpoints may be more cost-efficient in the short term, a cybersecurity incident is significantly more likely if no tools at all are used in order to protect sensitive data.
What is the most popular endpoint management tool used for remote employees?
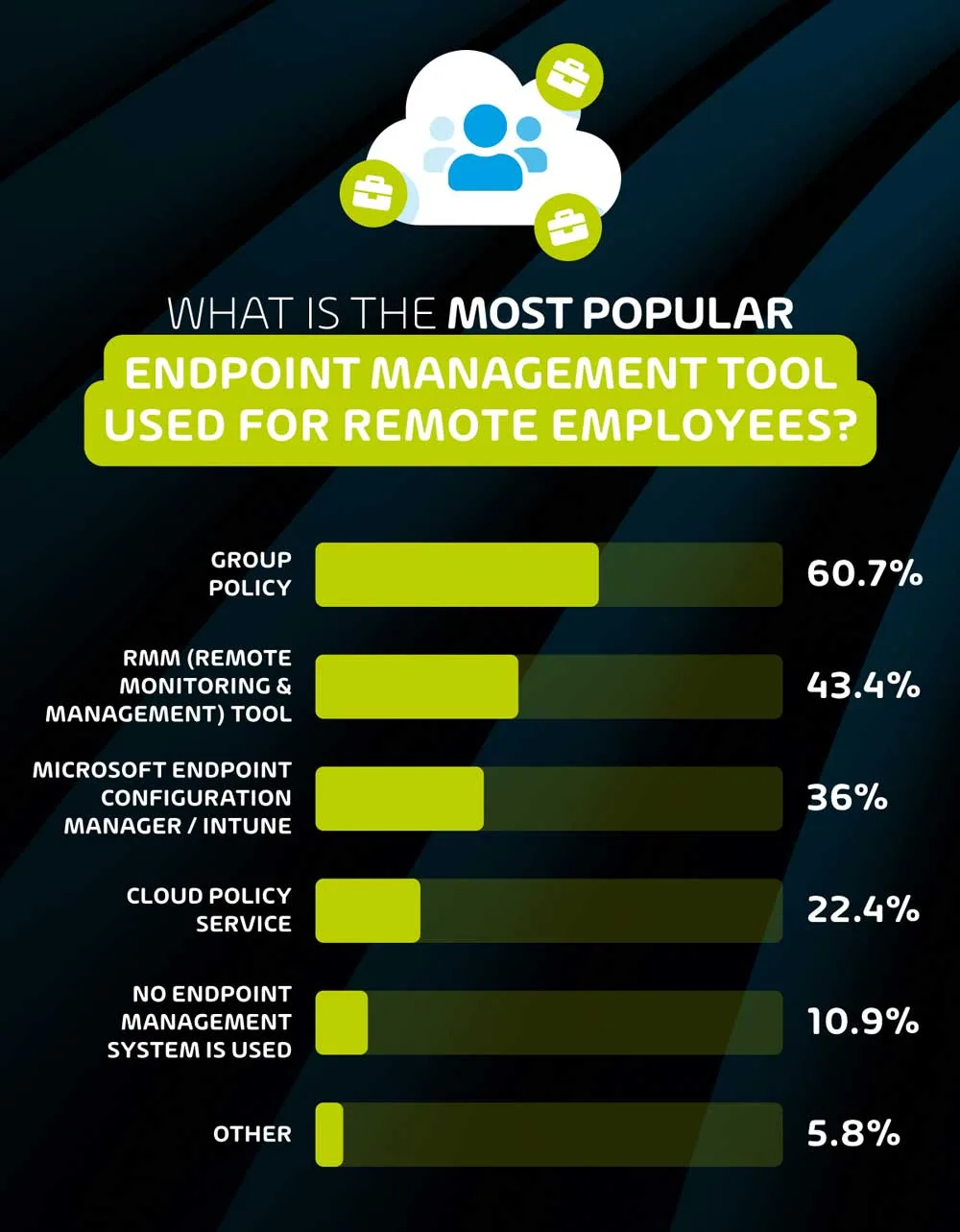
Group policy (60.7%) is the most popular endpoint management tool used by organizations, followed by RMM Tools (43.4%).
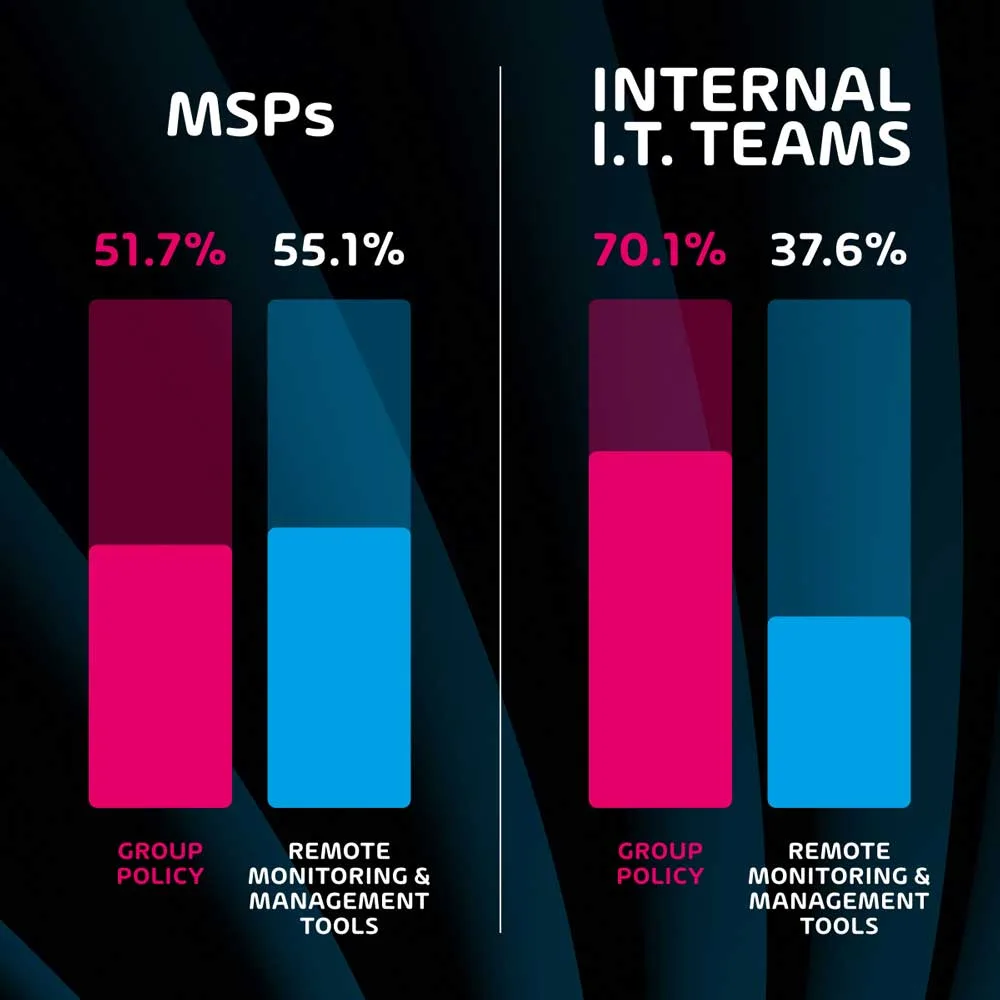
Endpoint management tools allow I.T. teams to be significantly more efficient when handling the security and monitoring of multiple endpoints. Group policy has been the go-to tool for many years, and this survey indicates that this is still the case among many organizations – especially those with internal I.T. teams as opposed to those that use MSP services.
The survey shows that 70.1% of internal I.T. teams use group policy for endpoint management, as opposed to 51.7% of MSP professionals. While group policy is still a valid tool for many organizations, it lacks features that are present on more modern remote monitoring and management tools. In fact, while group policy is the more popular endpoint management tool for internal I.T. teams, remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools are more popular among respondents that work for MSPs (55.1% vs 51.7%).
Over 1 in 10 respondents (10.9%) say that they do not use any endpoint management system.

Endpoint management systems are an extremely useful and basic tool for organizations and their I.T. service providers, however nearly 1 in 10 of our respondents say that their organization does not use any of the available systems. This is most prevalent among SMEs, where 15% of organizations with between 1 and 50 employees reported not using an EMS.

Employees are less confident in their company’s remote IT security than I.T. professionals.

In a curious twist, it seems that non-IT professionals are less optimistic about remote security than our surveyed I.T. professionals. 25.5% of non-IT professionals feel that their organization’s data is not secure while they work remotely, as opposed to only 17.9% of I.T. professionals who feel the same way.
There could be a few factors that explain this particular finding. We contacted behavioral & cyber profiling expert Mark T. Hofmann for his input, and this is what he had to say about the attitude of the various psychological profiles that can be found in the industry.
Psychological profiles of hackers and I.T. professionals
Hofmann quoted a 2020 study by Prof. Lawrence Sanders about the Psychological Profiling of Hacking Potential:
“The results suggest that individuals that are White Hat, Grey Hat and Black Hat hackers score high on the Machiavellian and Psychopathy scales. We also found evidence that Grey Hatters oppose authority, Black Hatters score high on the thrill-seeking dimension and White Hatters, the good guys, tend to be Narcissists.”
He goes on to say:
I can confirm this from my personal and professional experience and interviews with hackers:
Black Hats: Some “black hats” already have millions in their wallets but still commit crimes. If we conclude that cybercrime is mostly about money, this is only half the truth. There is always a motive behind the motive. If you are broke and need money, the motive is money. But if you already have a lot of money and keep going, the motive is not money but greed. It reminds me sometimes of gambling addiction. Thrill seeking is one of the most important psychological concepts to understand cybercrime.
Grey Hats: These are people between worlds. They commit crimes, but often have ideological motives or other ideals in doing so. Sometimes they are called hacktivists. If Robin Hood had been a hacker, he would have been a grey hat. But I find this definition difficult, because good and evil are subjective categories.
White Hats: Well, narcissism is not a black and white category, but a scale. In science, this is usually measured between 0-40. We are all somewhere on this scale and most of us reading this now are not “0”. So white hats are supposed to have somewhat above average scores as well… if two coders agree, one is not a coder. Mostly everyone thinks their own skills and approaches are right and everyone else is wrong. This might be true.
Full 2022 Remote Management survey results
If you’d like to take a look at the ransomware data, feel free to peruse the survey results here.
About the 2022 Remote Management survey respondents
Here’s a full breakdown of the survey respondents for full context of the ransomware data above.
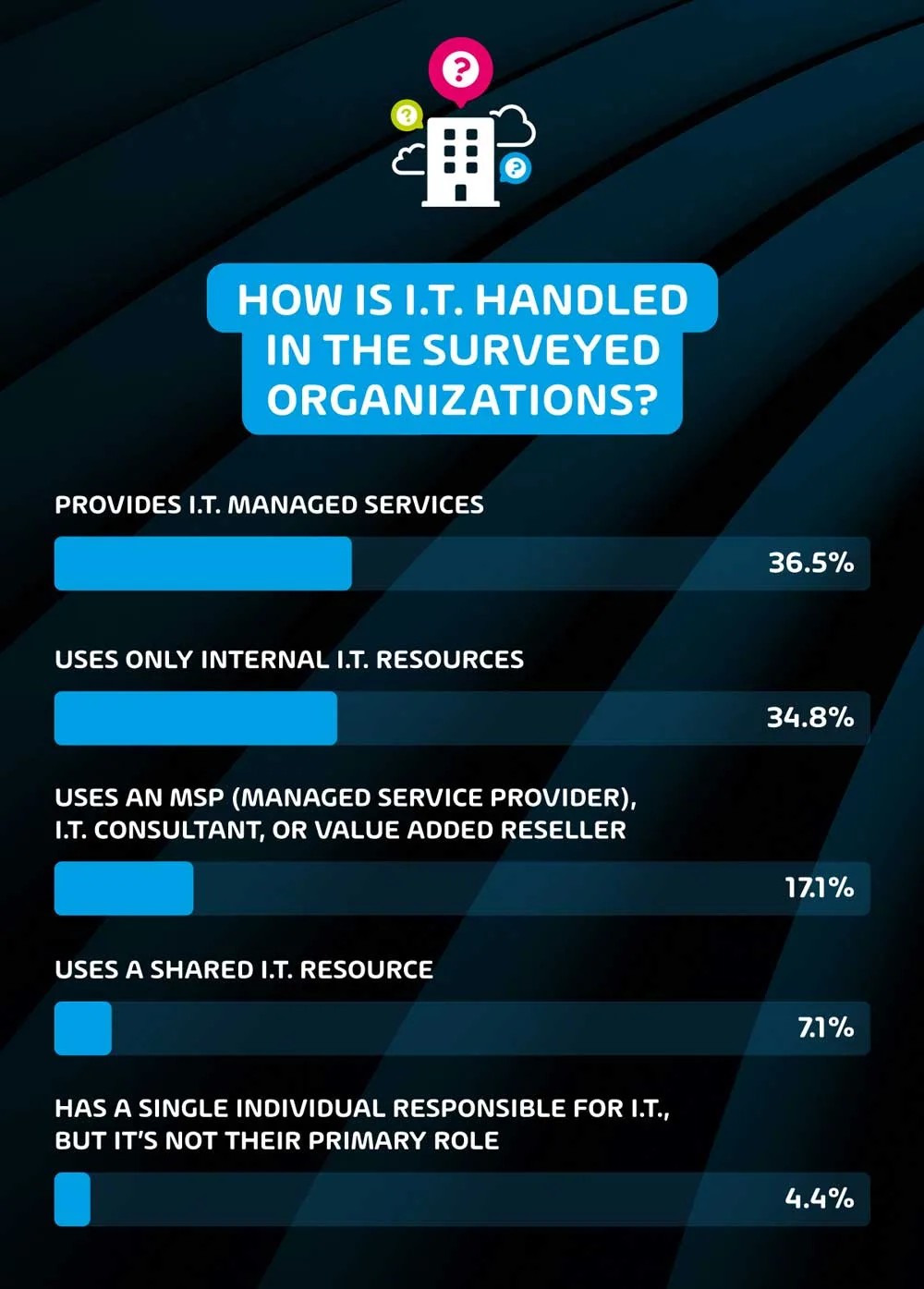
How is IT handled in the surveyed organizations?
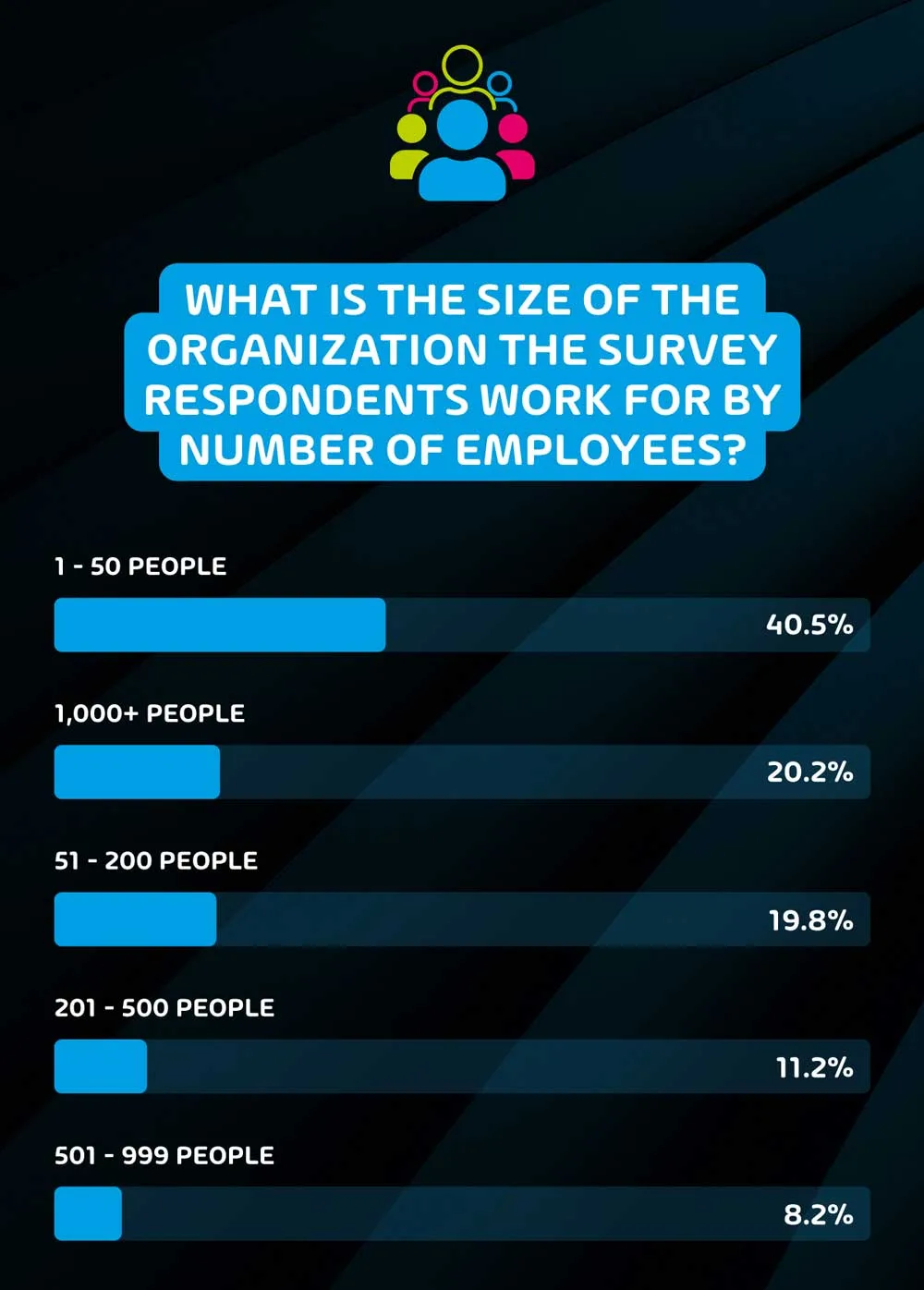
What is the size of the organization the survey respondents work for by number of employees?
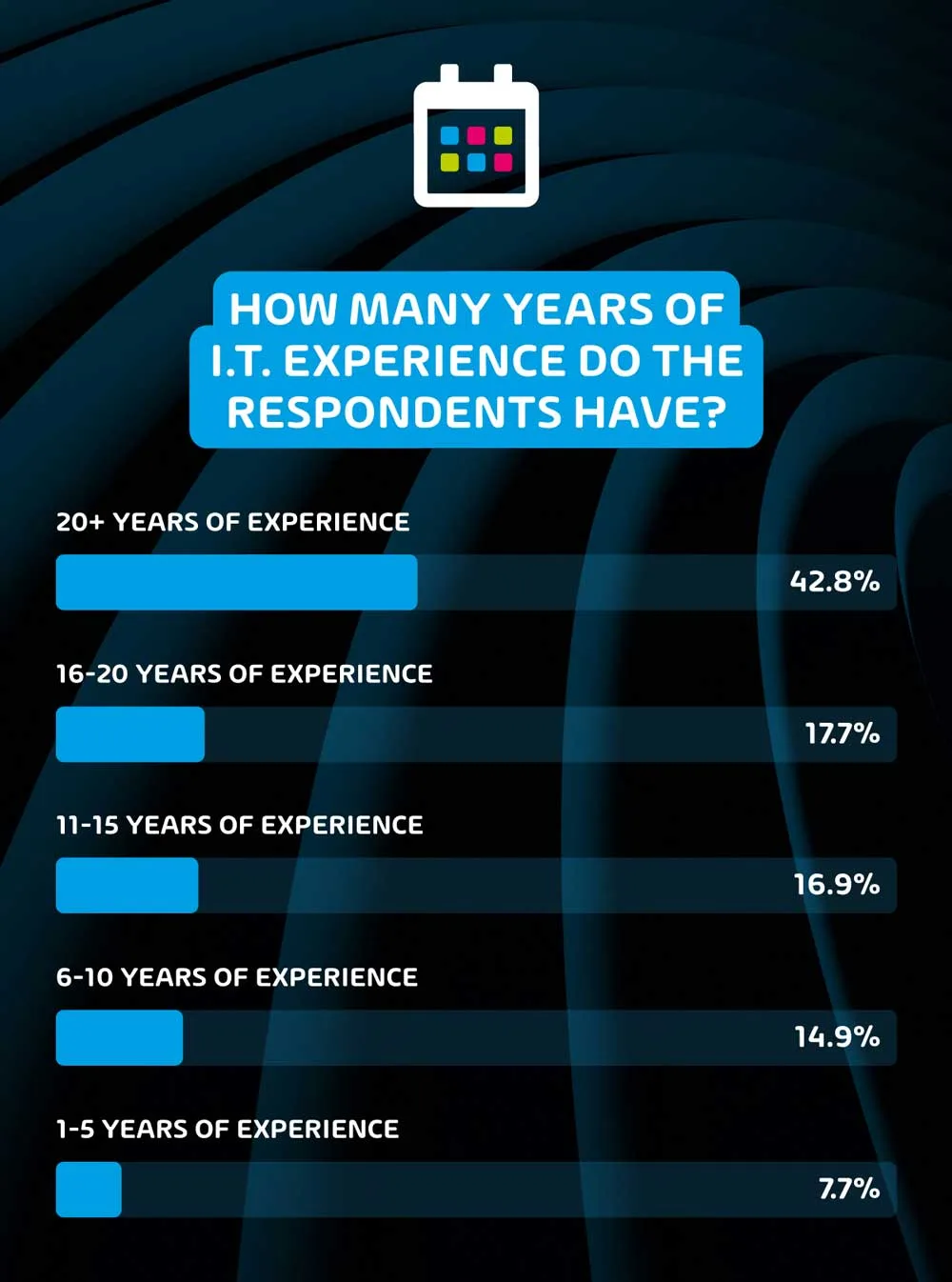
How many years of IT experience do the respondents have?
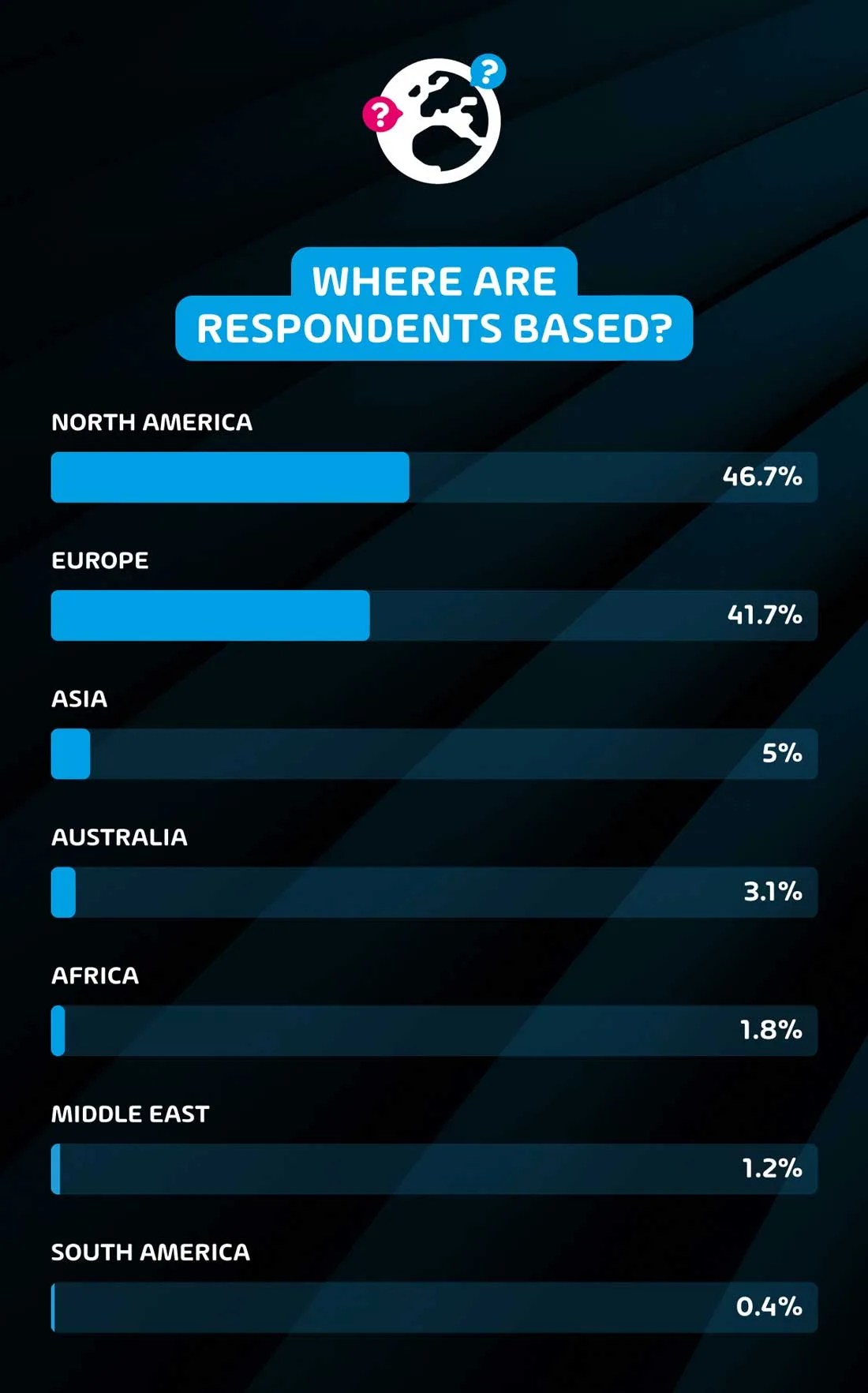
Where are the respondents based?
Conclusion
While we’re no longer in the immediate aftermath of the pandemic, it is clear through these survey results that organizations are still catching up with the changes that it brought with it from an I.T. infrastructure and security perspective. Many internal I.T. departments were completely unequipped to deal with the sudden shift towards hybrid and remote working when the pandemic hit, and while they tried their best to adapt from an operational perspective, security improvements to match the change are still lagging behind.

