

Security Alert: Microsoft Outlook Vulnerability
A severe security vulnerability has been discovered in Microsoft Outlook, which is currently being exploited by cybercriminals. The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2023-23397 with a CVSS score of 9.8, permits a remote, unauthorized attacker to compromise systems simply by transmitting a specifically crafted email. This malicious email enables the attacker to gain unauthorized access to the recipient’s credentials. Hornetsecurity detects emails that exploit the vulnerability and quarantines them to prevent emails from reaching the victim’s inbox.
The exploit is initiated by fetching and processing a malicious email by the Outlook client, potentially leading to exploitation even before the email is displayed in the preview pane. It triggers a connection from the victim to a location controlled by the attacker. This results in the leakage of the victim’s Net-NTLMv2 hash, a challenge-response protocol used for authentication in Windows environments. The attacker can then relay this information to another service and authenticate as the victim, further compromising the system.
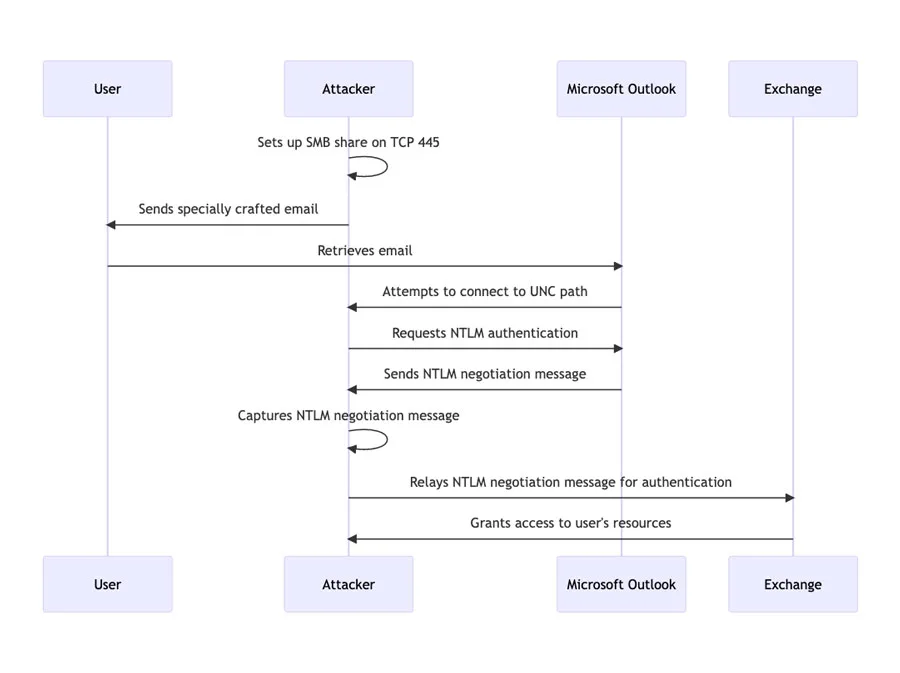
The complexity of the attack is low and it has been seen in the wild according to Microsoft, with the exploit being used to target the European government, military, energy, and transportation organisations. It was initially reported to Microsoft by CERT-UA (the Computer Emergency Response Team for Ukraine).
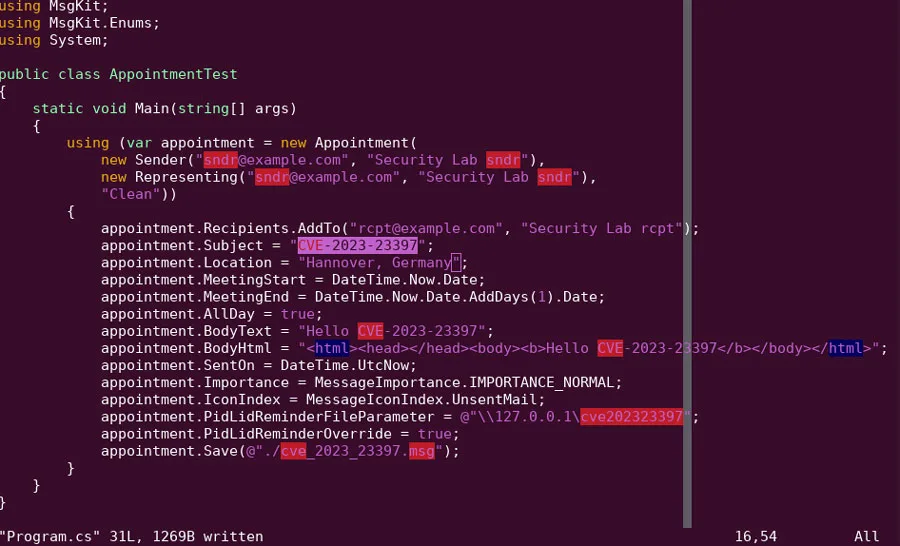
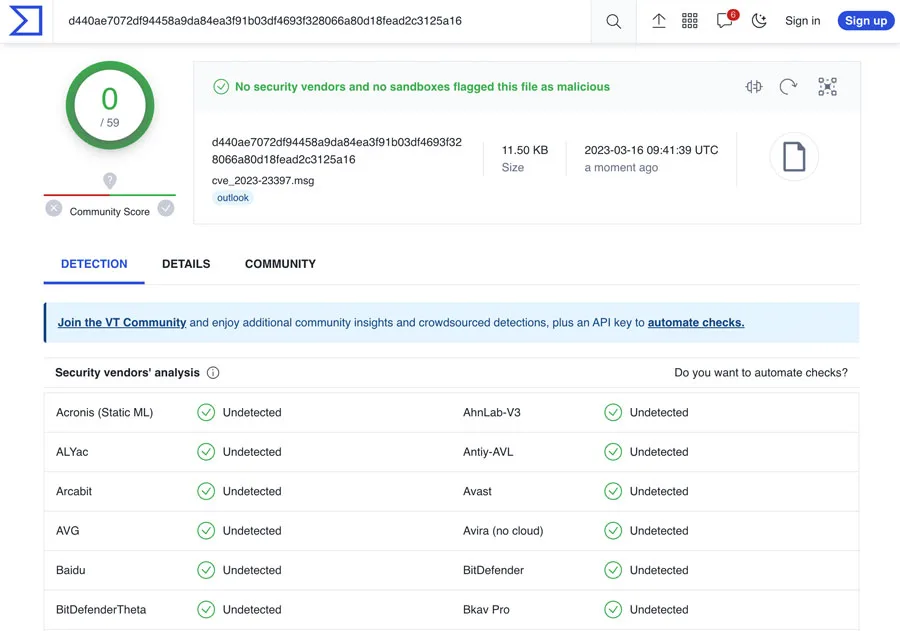
A proof-of-concept created by the Hornetsecurity’s Security Lab team demonstrates that the exploit is hard-to-detect since all anti-malware and sandbox services incorporated into VirusTotal were unable to recognize it as malicious.
Affected Versions
The critical Microsoft Outlook vulnerability impacts both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise. Additionally, Office 2013, 2016, and 2019, as well as LTSC editions, are susceptible to the attack.
Recommendations
Hornetsecurity’s users are protected by the Spam and Malware Protection and Advanced Threat Protection services against inbound threats. To better protect your organization, we recommend the following steps in accordance with Microsoft’s advice:
- Administrators should block TCP 445/SMB outbound traffic to the internet from the network using perimeter firewalls, local firewalls, and VPN settings. This action prevents the transmission of NTLM authentication messages to remote file shares, helping to address CVE-2023-23397.
- Add users to the “Protected Users Security Group” in Active Directory to prevent NTLM as an authentication mechanism. This approach simplifies troubleshooting compared to other methods of disabling NTLM. It is particularly useful for high-value accounts, such as domain administrators.
- Microsoft has provided a script to identify and clean up or remove Exchange messages with UNC paths in message properties. The script can be found at https://microsoft.github.io/CSS-Exchange/Security/CVE-2023-23397/. Administrators should apply the script to determine if they have been affected by the vulnerability and to remediate it.
The likelihood of more widespread attacks targeting the CVE-2023-23397 vulnerability is expected to increase as public proof-of-concepts are already released. We therefore highly recommend that all users of Microsoft Outlook apply the security patches provided by Microsoft as soon as possible.
The Security Lab at Hornetsecurity continues to monitor the threat landscape to ensure that our customers are protected from the latest cyber threats.


