

Businesses Are Feeling the Ransomware Impact in 2025 More Than Ever Before
In recent years, ransomware attacks had been waning but in 2025 it’s making a sharp comeback. For the first time since 2022, the number of organizations hit by ransomware is climbing again, with 24% reporting an attack this year compared to just 18.6% in 2024. This reversal of a downward trend signals more than just bad luck – it highlights a renewed wave of criminal innovation.
With attackers leaning on automation, exploiting weak patching, and abusing unsecured devices, ransomware has reasserted itself as one of the most disruptive cyber threats facing organizations today. In this article, we review the key takeaways from the Ransomware Impact Report 2025 and why 2026 will mark a significant crossroads for the future of the threat.
The State of Play in 2025
Ransomware continues to evolve and in 2025, it’s not just persisting, it’s resurging. As one of the most disruptive threats to organizations worldwide, ransomware has reasserted itself with increased sophistication and reach.

Ransomware Impact Report 2025
Ransomware attacks are increasing for the first time in 3 years, reaffirming its status as one of the most persistent threats to businesses in 2025.
Find out how organizations are adapting, what emerging trends are, and where new risks lie.
Amidst the rise in ransomware, concerns around cybersecurity generally are growing. 76% of security managers believe that a major cyberattack is likely within the next 12 months. This perception has risen sharply, echoing the resurgence in attacks identified in our report.
A sharp reversal of the downward trend
This year’s findings show a sharp reversal of the downward trend in attack frequency, highlighting both the growing scale of ransomware operations and the urgent need for updated defenses.
This increase appears driven by 2 key factors:
- Greater attack automation
- A broader range of tactics being used by cybercriminals
While traditional phishing remains the leading attack vector (reported by 46% of respondents), the data shows a growing reliance on compromised endpoints (26%) and stolen credentials, often linked to poor patching practices and unsecured « Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) » environments.

Despite the rise in attack volume, fewer organizations are paying ransoms, suggesting better recovery preparedness or a growing reluctance to engage with extortionists. However, the financial and operational impact of attacks remains severe, especially as ransomware becomes more targeted and persistent.
Why resilience matters more than ever
Ransomware is a highly destructive form of malware that locks organizations out of their data and systems, with threat actors demanding payment, often in cryptocurrency, in exchange for restoration.
The consequences can include data loss, downtime, regulatory penalties, and reputational harm. According to the 2025 Proofpoint Voice of the CISO report, 66% of companies have recently suffered a loss of sensitive data. This figure, which is significantly higher than last year, highlights the need to strengthen resilience, as discussed in our study.
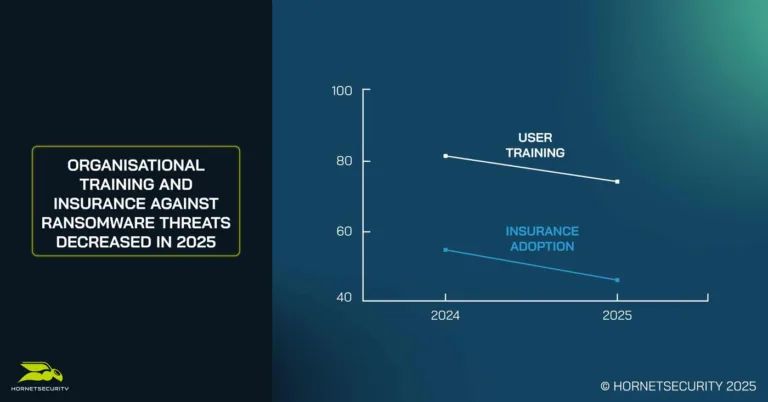
In addition, 58% of CISOs feel inadequately prepared for cyber threats, despite widely deployed DR plans. This year, respondents also offered insight into their evolving cybersecurity strategies. Investments in endpoint detection tools, regular backups, and user awareness training continue to be key pillars of ransomware defense.
But with the rise in credential-based attacks and software exploits, the findings stress the importance of adopting multi-layered security architectures and zero-trust principles.
As ransomware tactics grow more complex and multifaceted, organizations must stay ahead, not only by defending against initial breaches, but by building resilient systems capable of swift recovery when incidents occur.
Credential Attacks Growing Along with Ransomware
The renewed rise in ransomware attacks is closely tied to attackers adopting greater automation and AI-enhanced methods, enabling them to scale operations while maintaining precision. Sophistication continues to increase, particularly in terms of how attackers identify and exploit vulnerabilities in hybrid IT environments.
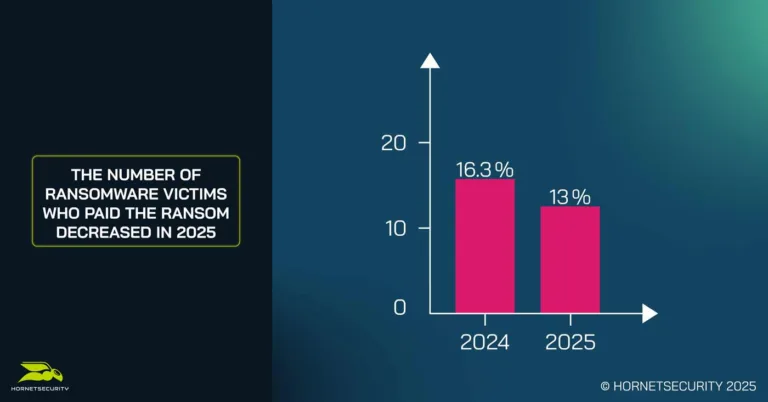
Interestingly, while fewer victims are paying ransoms, with only 13% reporting that they paid to recover their data, compared to 16.3% in 2024, the overall impact remains significant. Attackers are causing widespread disruption, with exfiltration and data destruction used as leverage even when payments aren’t made.
AI Amplifying the Threat
A defining feature of ransomware this year is the growing integration of AI tools into attack strategies. The growing adoption of GenAI and collaborative tools exposes organizations to new risks: 60% of CISOs perceive generative AI as a security threat, and 68% are investing in AI-powered detection and protection capabilities. In addition to this:
- 77% of CISOs surveyed identified AI-generated phishing as a real and growing threat;
- 61% believe AI has significantly increased the risk of ransomware attacks overall.
Attackers are now using generative AI to create:
- Highly customized phishing emails;
- Deepfake audio and video for social engineering;
- Automated, multi-vector intrusion strategies.
This level of automation and deception has rendered traditional detection methods less effective, requiring a shift toward EDR/XDR platforms, zero-trust frameworks, and automated anomaly detection.
Shifting Entry Points: Beyond Phishing
While phishing remains the top initial access vector, its dominance is waning slightly. This year:
- Phishing email-based attacks dropped to 46% (from 52.3% in 2024);
- Compromised endpoints now account for 26% of ransomware delivery;
- Stolen credentials were involved in approximately 25% of attacks;
- Exploited vulnerabilities contributed to 12%.
These changes highlight a strategic shift by threat actors, targeting organizations where multi-factor authentication (MFA) is weak, patching is inconsistent, and shadow IT remains pervasive, especially in remote and hybrid work environments.
Training Gaps and “False Compliance”
Although 74% of organizations report offering end-user training against ransomware, 42% of security leaders admit that their training is insufficient or ineffective.
This disconnect has created a worrying phenomenon: “false compliance”, where organizations meet superficial awareness standards but lack meaningful engagement or retention of best practices.
Small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) are particularly at risk, often conducting annual, checkbox-style training sessions with little follow-up. This contributes to persistent human error as a vulnerability, especially when facing advanced phishing and social engineering tactics.
According to Proofpoint, human error remains the dominant source of incidents: 66% of CISOs identify the human factor as the primary risk, particularly in terms of data leaks and internal compromise. Although training is improving, it often remains superficial (42% consider it inadequate).
These findings corroborate Hornetsecurity’s conclusions on the limitations of “compliance tick-box” programs.
How to Protect Your Business from Ransomware
Ransomware attacks are rising fast, but you don’t have to face them unprepared. With Hornetsecurity Advanced Threat Protection, you can enhance your security in several ways:
- Defend against ransomware to protect sensitive information and keep your data safe;
- Feign facts identification allows for identity-independent content analysis of news, helping you spot any falsified information;
- Targeted attack detection focuses on identifying specific attacks on individuals who may be particularly at risk;
- Intention recognition system provides alerts for content patterns that suggest malicious intent, keeping you informed of potential threats;
- Identity spoofing recognition helps detect and block forged sender identities, adding an extra layer of security;
- Fraud attempt analysis checks the authenticity and integrity of metadata and email content, ensuring that you can trust the information you receive.

Don’t wait until it’s too late – schedule your free demo today and see how Hornetsecurity can protect your business against ransomware attacks.
Conclusion
The numbers tell a clear story: ransomware isn’t fading into the background; it’s resurging with greater force and sophistication. The last three years have shown how quickly the threat landscape can shift, and 2025 proves that complacency is dangerous.
Organizations must act now to update defenses, strengthen endpoint protection, and raise employee awareness. Preparing today doesn’t just reduce the risk of falling victim, it builds resilience against the next generation of attacks that are already on the horizon.
FAQ
Ransomware is resurging due to increased attack automation and a wider range of tactics employed by cybercriminals. This includes the exploitation of unsecured devices and weak patching practices, resulting in a significant uptick in attacks.
No, fewer organizations are paying ransoms in 2025, with only 13% doing so compared to 16.3% in 2024. This may indicate improved recovery efforts or a reluctance to engage with extortionists, despite the significant impact of attacks.
Organizations should focus on building resilience by strengthening endpoint protection, adopting multi-layered security architectures, and investing in user awareness training to better prepare for evolving ransomware threats and minimize risk. Remember, with Hornesecurity, you can always count on our Advanced Threat Protection to have your back.
To protect from ransomware, regularly back up data, use robust antivirus software, keep systems updated, and educate employees about phishing attacks. Implement strong access controls and network segmentation to minimize risk.
Enterprises are more susceptible to ransomware due to outdated systems, lack of employee training, inadequate security measures, and insufficient backup protocols. High-value data and critical operational dependencies also make them attractive targets.
The consequences of a ransomware attack can be devastating including:
– data loss;
– financial losses from ransom payments;
– operational downtime;
– damage to reputation;
– potential legal implications due to data breaches and regulatory violations.
