
Spear Phishing
What is a Spear Phishing attack?
In this article, you’ll learn what spear phishing is, how it differs from regular phishing, and why it’s a growing threat to businesses. We’ll look at how these attacks work, common techniques used and the warning signs to look out for.
What is Spear Phishing?
Spear phishing is a form of social engineering, often involving the impersonation of an individual to trick the recipient into performing a desired action, usually financial in nature. Often a hacker will pretend to be someone the victim knows, such as a colleague, manager, customer or supplier.
Unlike traditional phishing emails, spear phishing emails actually target people who would normally treat fake emails with a healthy degree of scepticism. This means that spear phishing emails are much more effective at building trust. In particular, it exploits the recipient’s good faith by making them believe they are safe – for example, because of seemingly familiar sender addresses or the reputation of the company named in the email.
With this successful deception, the cybercriminal can now take the spear phishing attack to the next level. The unsuspecting victim will only discover the ruse much later, when it is usually too late to react.
This is how a spear phishing attack works in practice
Once the victim has received a deceptive email, they may be tricked into downloading a link that installs carefully hidden malware. Alternatively, a link may take the victim to a bogus website where a form is filled in to collect personal information.
In recent years, it has become increasingly apparent that spear phishing is no longer limited to email communication. Social channels are also being used for this type of attack. Once the link or malware has been planted on the potential victim’s computer, the cybercriminal can simply sit back and wait.
Spear phishing vs phishing
Spear phishing and phishing attacks both use impersonation to commit fraud. The difference between the two is that spear-phishing emails impersonate people, while phishing emails impersonate brands. Unlike phishing, spear phishing targets a single individual, contains no links or attachments in the email, and typically contains a request for a wire transfer, gift cards, or direct deposit changes rather than account information. Below are just two examples of a phishing email versus a spear phishing email:
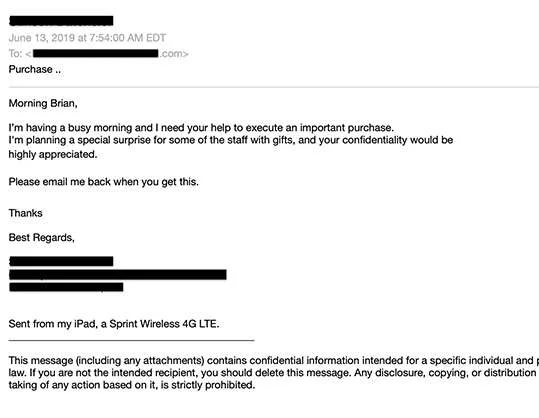

The Targets of Spear Phishing
Attackers usually find out about their target beforehand. First name, last name, date of birth, place of residence, street, hobbies and information about family members, friends and business associates are all easy to find on the Internet. There are countless publicly accessible databases. In most cases, it is the users themselves who ensure that their profile information is freely visible to third parties. This is particularly true of social media.
The attacker also learns information such as the preferences and habits of the target, for example by seeing what online purchases they have made at what time on eBay or Amazon. Even tracking movement patterns is no longer a major challenge for cyber criminals. With GPS, many users of so-called tracking services can even help an attacker find out exactly where a user is, when they are there and for how long.
Phishing/social engineering accounted for 52% of cyberattacks against SMBs in 2018 – Keeper/Ponemon
The continuum of email spoofing used
To trick recipients into thinking they’re reading an email from a trusted sender, spear phishers use a technique called “spoofing” that allows them to impersonate a legitimate sender and email address. There are three primary methods of email spoofing :
Display Name Spoofing
Display name spoofing impersonates the sender’s name, but not the email address. This is effective because many users trust the sender immediately when they see the name. It’s also effective because many email clients, especially on mobile phones, only display the sender’s name, not the email address.
Domain spoofing
This method is more sophisticated than display name spoofing but also easier to detect by SPF (Secure Policy Framework), DMARC (Domain Message Authentication Reporting), and DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Email). With domain spoofing, a spear phisher can specify the email address they want to spoof. When an email address is an exact replica of a trusted sender, users are unlikely to recognize that the email is spoofed.
Cousin Domains
A close cousin email address is nearly identical to a legitimate one, with only a slight modification. In the past, close cousin spoofing attempts were more obvious, such as mIcrosoft.com instead of microsoft.com. Today, attempts are more advanced and difficult to spot, such as user@mycompanyltd.com instead of user@mycompany.com. These subtle changes can be extremely difficult to spot for busy staff who quickly read and respond to emails, especially when they are urgent in nature. Moreover, DMARC and SPF are ineffective against close cousins because they only protect exact domains.
Spear Phishing Examples
There is no shortage of ways to trick people into giving up sensitive data and credentials. However, there are some well-honed attacks that spear phishers turn to time and again.
- Direct Deposit Changes
In one version of this scam, a hacker posing as an employee sends an email to an HR assistant, requesting to change their bank account for their payroll direct deposit. In another version, a hacker posing as a vendor emails a staff member in accounting, informing them that the company’s bank account and routing number has changed, and future payments should be sent to the new account. - Gift Card Requests
Posing as an executive, a hacker asks an employee to purchase multiple gift cards and send them the codes on the back of the cards. Often, a hacker will say that they’re in a meeting or away from their office. This adds to the believability of an executive writing an email from a personal email address, such as Gmail or Yahoo. - W-2 Spear Phishing
A spear phisher posing as an executive emails a staff member in the HR department, requesting employee W-2s, a US tax form reflecting employee earnings and tax deductions. Tax time is particularly stressful for accounting and HR departments, and the pressure, in addition to the time constraints, makes them vulnerable to making the mistake of falling for this type of attack. - Multiphase Attacks
A common method for hacking into Microsoft 365, multiphase attacks begin with phishing and evolve into spear phishing. A hacker sends a phishing email to an employee, impersonating Microsoft. The victim unknowingly gives up their Microsoft 365 login credentials on a phishing page. Armed with the victim’s username and password, the hacker enters the business’s Office 365 ecosystem where they launch spear phishing attacks using legitimate Microsoft 365 email addresses. - Wire Transfer Requests
Also known as business email compromise (BEC), this spear phishing variant is one of the most costly. A hacker posing as a top executive makes a request for funds in the form of a wire transfer. In many high-profile cases, businesses were completely unaware that millions of dollars had been sent to fraudulent bank accounts.
Spear Phishing Techniques to look out for
A one-off, text-only spear phishing email might look unsophisticated on the surface, but there are social engineering techniques at work that reveal a sophisticated level of psychological manipulation. Below are some examples :
- Engaging in pretexting
Spear phishers prime their victims by first sending a friendly email and engaging in small talk, such as “how was your vacation?” or “congrats on the promotion.” This lowers the victim’s guard, prepping them for the spear phisher’s eventual request, which might not come for several more emails. - Making urgent requests
Often, spear phishers will convince their victims that they have only hours—or even minutes—to send a wire transfer, change their bank account information, or purchase gift cards for clients. - Sending emails via mobile
Spear phishers posing as executives often claim to be out of the office, even out of the country, and urgently need the victim’s help. Adding “sent from my iPad, iPhone, or Android device” adds to the believability of such a claim and also excuses mistakes in the email, such as typos. It also creates an excuse for using a non-corporate email address like Gmail.
(Digital) Sources for Spear Phishing
Attackers often look for reviews on travel portal pages. Online hotel guest books can give a very detailed overview of a person’s financial background. In this way, specific conclusions can be drawn quickly about interrelationships among business and private areas. However, this is only a digital search for information.
In any case, employees who freely disclose personal data increase the risk of being affected by a spear phishing attack. Because those in the company who handle their data carelessly are ideal targets, spear phishers specific look for employees with such vulnerabilities.
The Immediate Environment of the Spear Phishing Victim
Cybercriminals are always clever when it comes to finding more detailed information. For this reason, spear phishing attacks often target the immediate environment of the potential victim. It is not uncommon for sensitive documents to be intercepted directly from a company’s paper shredder or even from an employee’s home.
Once the attacker has all the information they need, they proceed with the spear phishing attack. In the next phase, one or more employees receive emails asking them to confirm certain information. This stage also includes a blurring of the line towards CEO fraud, as the emails are usually spoofed with sender addresses from government agencies.
Attached files used in everyday business emails are often used as a gateway. A Word, Excel or PDF file can be the key to the entire corporate network. Most people who open these attachments have no idea of the potential danger.
The Bait in a Spear Phishing Attack
The design and camouflage of the lure is a critical element in deceiving the target of a spear phishing attack. The more convincingly an attacker disguises the bait, the greater the likelihood of success.
While spear phishing attacks in the past were often limited to email, today’s focus is increasingly on social media. Here too, company employees may unknowingly interact with spear-phishers on a personal level, resulting in the victim communicating directly with the attacker. Again, this is an opportunity for victims to be spied on.
Professional spear phishing attacks are difficult to detect. The content is usually so targeted that it is very difficult for lay people to recognise. This is where spear phishing differs from normal phishing, where countless emails are sent indiscriminately in a so-called “shotgun tactic”.
How can companies protect themselves from a Spear Phishing attack?
Spear phishing attacks are a particular challenge for corporate IT security officers. After all, the individual employee is the central weak point. Links and file attachments are recklessly opened without recognising the real sender.
The same applies to false friend requests received via social networks. The recipient’s psyche is used as a gateway, bypassing their innate scepticism. Because it is so effective, the number of spear phishing attacks is increasing every year, so it is extremely important to educate and raise awareness of the dangers of spear phishing.
Unmask Spear Phishing Attacks
In order to protect yourself against spear phishing, e-mail notifications that request the disclosure of sensitive data should be ignored.
Neither a financial institution nor a service provider would ever ask their customers to reveal personal information via email.
The same applies to questionable messages or allegedly harmless links from alleged social media acquaintances—and in particular to cryptic addresses or URLs. But be aware that links that appear trustworthy can also be problematic.
Use Social Media With Caution
Perhaps you have seen a post on a pinboard on Twitter or Facebook that contained personal data. There are the strangest cases—from publishing a driver’s license to disclosing a bank statement, everything is out there. Even people presenting credit cards! Such people are just begging for a spear phishing attack.
Under certain circumstances, data can also be tapped using image recordings. This is especially true when sensitive documents are on a desk and end up as a photo on social media. Such cases must result from an employee who thoughtlessly posts a picture of his workplace. This scenario can often be found in practice.
Using traditional Email Defense
Reputation
Reputation-based threat detection blocks known, malicious email senders (IP addresses) and phishing URLs. A reputation-based filter will block bad senders known to the filter but will miss new threats.
Secure Email Gateways
Secure email gateways (SEG) rely on reputation and signature-based detection. A SEG sits outside of Microsoft 365 architecture, disabling Exchange Online Protection (EOP) and leaving Microsoft 365 unprotected against insider attacks.
Signatures (Fingerprint)
Signature-based threat detection blocks threats with a known “signature,” such as malware code.
Sandboxing
Sandboxing sends suspicious emails to a controlled environment for analysis. It’s ineffective against spear phishing emails that do not include attachments or links.
Using predictive defense
With predictive defense, artificial intelligence (AI), including a combination of supervised and unsupervised machine learning models, work together to identify the telltale and difficult-to-detect signs of spear phishing :
Supervised Learning
Algorithms are trained with malicious and legitimate and emails to recognize specific features of spear phishing emails, such as mobile signatures and email addresses from public domains.
Unsupervised Learning
Natural Language Processing and Unsupervised Anomaly Detection recognize abusive patterns in spear phishing emails, including urgency, flag words, and email addresses that do not match senders in a business’s entity model.
Signatures (Fingerprint)
Signature-based threat detection blocks threats with a known “signature,” such as malware code.
User Feedback Loops
Users report spear phishing emails to the security operations team (SOC), which analyzes the email and improves the algorithms.
Protect your Buisness with 365 Total Protection
Hornetsecurity for M365 blocks advanced attacks from the first email thanks to machine learning models that perform real-time behavioral analysis of the entire phishing email, including any URLs and attachments. Our AI-based threat detection stops threats before, during, and even after phishing attacks.
Learn about HORNETSECURITY’S SERVICES
Interested in Related Topics?
Did you like our contribution to spear phishing? Then other articles in our knowledge base might interest you as well! We help you learn more about cybersecurity related topics such as Emotet, Trojans, IT Security, Cryptolocker Ransomware, Phishing, GoBD, Cyber Kill Chain and Computer Worms.



